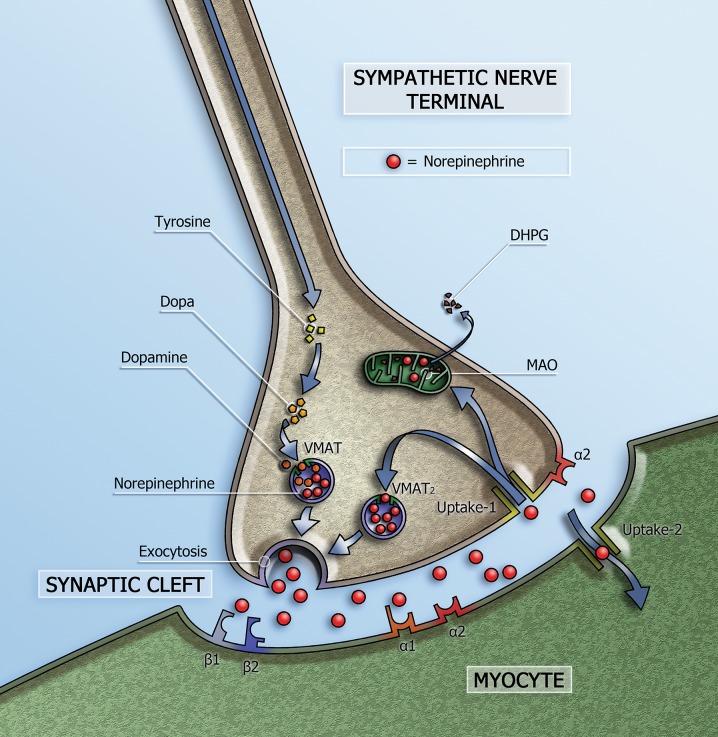
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the sympathetic synapse. Norepinephrine is synthesized within neurons by an enzymatic cascade. Dihydroxyphe-nylalanine (DOPA) is generated from tyrosine and subsequently converted to dopamine by DOPA decarboxylase. Dopamine is transported into storage vesicles by the energy-requiring vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT). Norepinephrine is synthesized by dopamine β-hydroxylase within these vesicles. Neuronal stimulation leads to norepinephrine release through fusion of vesicles with the neuronal membrane (exocytosis). Apart from neuronal stimulation, release is also regulated by a number of presynaptic receptor systems, including α2–adrenergic receptors, which provide negative feedback for exocytosis. Most norepinephrine undergoes reuptake into nerve terminals by the presynaptic norepinephrine transporter (uptake-1 mechanism) and is re-stored in vesicles (following uptake by vesicular amine transporter 2 (VMAT2)) or is metabolized in cytosol dihydroxyphenylglycol (DHPG) by monoamine oxidase (MAO)