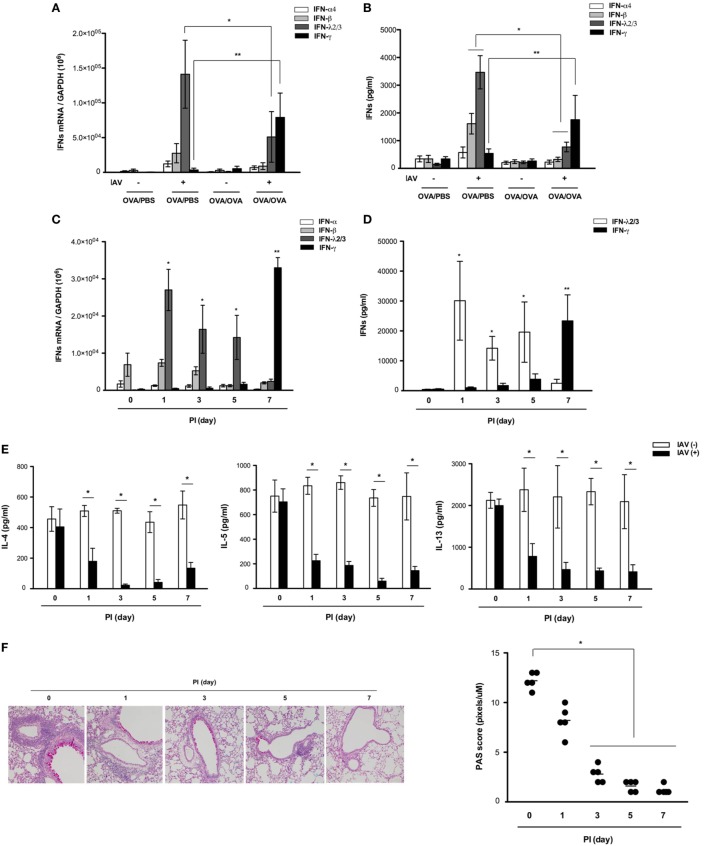
Figure 3.
Expression and secretion of various interferons (IFNs) after influenza A virus (IAV) infection of non-asthmatic and asthmatic mice. Non-asthmatic (N = 5) and asthmatic mice (N = 5) were infected with 213 pfu IAV WS/33 (H1N1). The mRNA levels in the lung (A) and levels of secreted IFN-α, IFN-β, IFN-λ2/3, and IFN-γ in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid (B) were determined by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, respectively, at 7 days after infection. The mRNA levels and levels of secreted IFN-α, IFN-β, IFN-λ2/3, and IFN-γ in the lung (C) and BAL fluid (D) were determined in IAV-infected asthmatic mice until 7 dpi. A multiplex assay was performed to quantify the levels of secreted Th2 cytokines in the BAL fluid of IAV-infected asthmatic mice until 7 dpi (E). Histological assessment was performed using periodic acid Schiff (PAS)-stained lung sections of asthmatic mice (N = 5) (F) harvested at 0 (N = 5), 1 (N = 5), 3 (N = 5), 5 (N = 5), and 7 (N = 5) dpi. Micrographs shown are representative of five mice. PCR, plaque assay, and multiplex assay results are presented as mean ± SD from five independent experiments (*,**p < 0.05 compared with the levels in non-asthmatic and asthmatic mice at 7 dpi, Figures 2B–D *IFN-λ2/3, **IFN-γ).