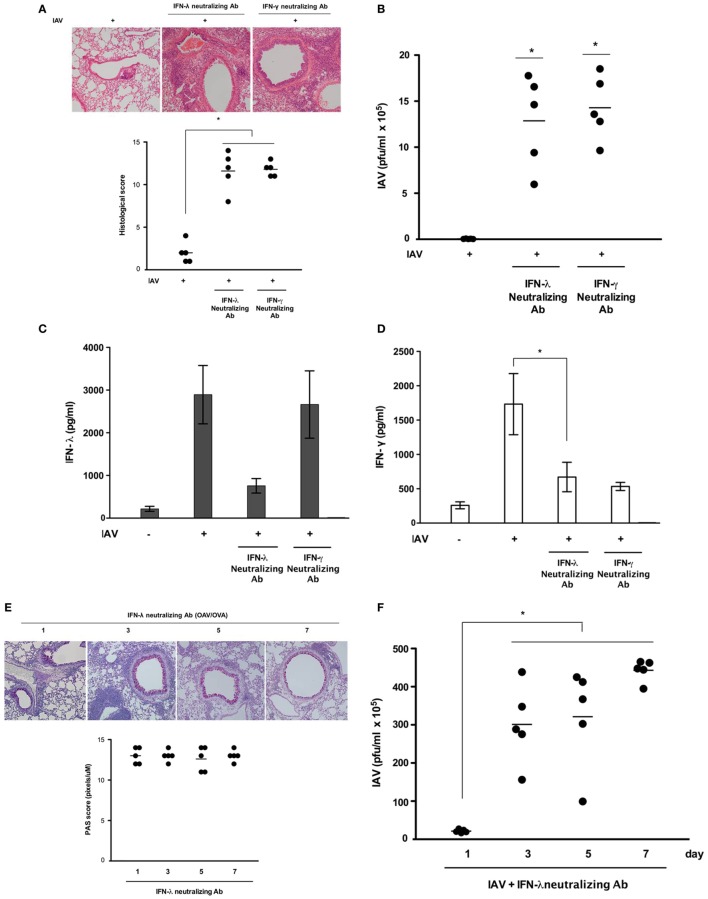
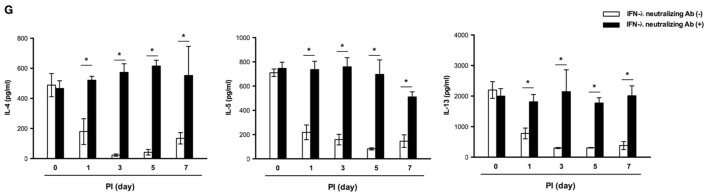
Figure 4.
Acute influenza A virus (IAV) infection is aggravated in asthmatic mice administered neutralizing antibodies against interferon (IFN)-λ2/3 and IFN-γ. Asthmatic mice with isotype-control (rat IgG) antibodies were infected with 213 pfu IAV WS/33 (H1N1) (N = 5) and treated with neutralizing antibodies against IFN-λ2/3 (N = 5) or IFN-γ (N = 5). Hematoxylin/eosin (H&E)-stained micrographs were generated from lung sections obtained from IAV-infected asthmatic mice on day 7 (A). Viral titer (B) and secreted IFN level (C,D) were determined by plaque assay and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Histological assessment was performed using periodic acid Schiff (PAS)-stained lung sections of asthmatic mice (N = 5) (E). Viral titer (F) and Th2 cytokine levels (G) were assessed using a plaque assay and a multiplex assay at 0 (N = 5), 1 (N = 5), 3 (N = 5), 5 (N = 5), and 7 (N = 5) dpi. Micrographs shown are representative of lung sections from five mice. Polymerase chain reaction, plaque assay, and multiplex assay results are presented as mean ± SD from five independent experiments (*p < 0.05 compared with the values of mice treated with IgG and neutralizing antibodies).