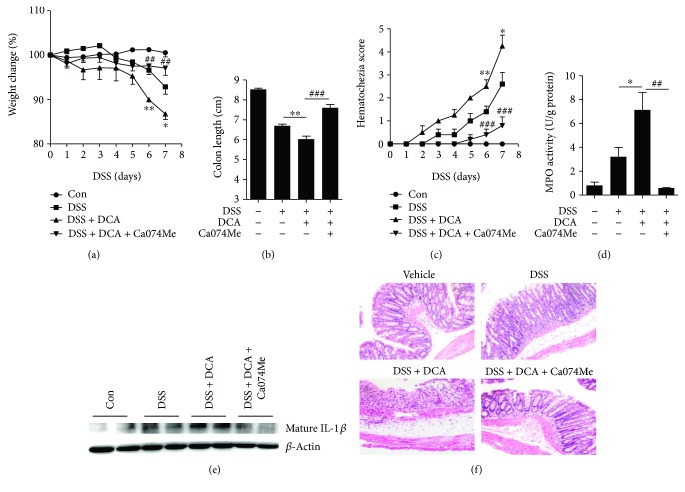
Figure 4.
DCA administration exacerbates DSS-induced colitis and inhibition of cathepsin B release reverses the intestinal inflammation. Colitis was induced in mice with 2.5% DSS and animals were divided into control, DSS-treated, DSS-treated plus DCA enema, DSS-treated plus DCA enema, and cathepsin B inhibitor (Ca-074Me)-injection groups. (a) Loss of basal body weight, (b) colon length, (c) hematochezia score, and (d) MPO activity in colon tissue were detected. (e) Immunoblot analysis of mature IL-1β (17kD) in colonic homogenates. (f) HE staining of distal colon sections of differently treated mice. ∗ p < 0.05 and ∗∗ p < 0.01 compared to the DSS-treated alone mice. # # p < 0.01 and # # # p < 0.001 compared to the DSS-treated plus DCA enema mice. Error bars indicate s.e.m. The data shown are from 3 individual experiments.