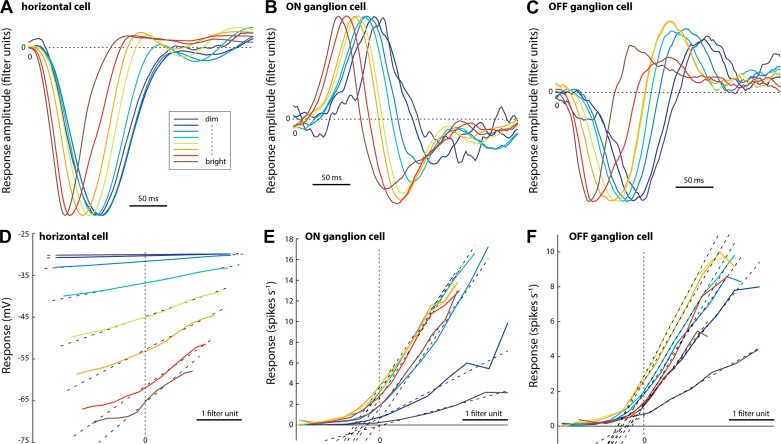
Fig. 2.
Light adaption impacts both linear and nonlinear response properties of horizontal cells and ganglion cells. A–C: temporal response characteristics (linear filters) of a horizontal cell (A), an ON-type ganglion cell (B), and an OFF-type ganglion cell (C). Each panel shows a single-cell example representative of the recorded population. Filters were calculated from the response to binary white noise (70% contrast) at different mean light levels (for values, see Fig. 1A legend). Filter amplitude is normalized to the first peak. D–F: static nonlinear transfer functions (see methods) obtained using the linear filters shown in A–C. Dotted lines show linear fits to the data from 15% to 85% of the cell’s dynamic response range used to measure contrast gain and response linearity at each light level.