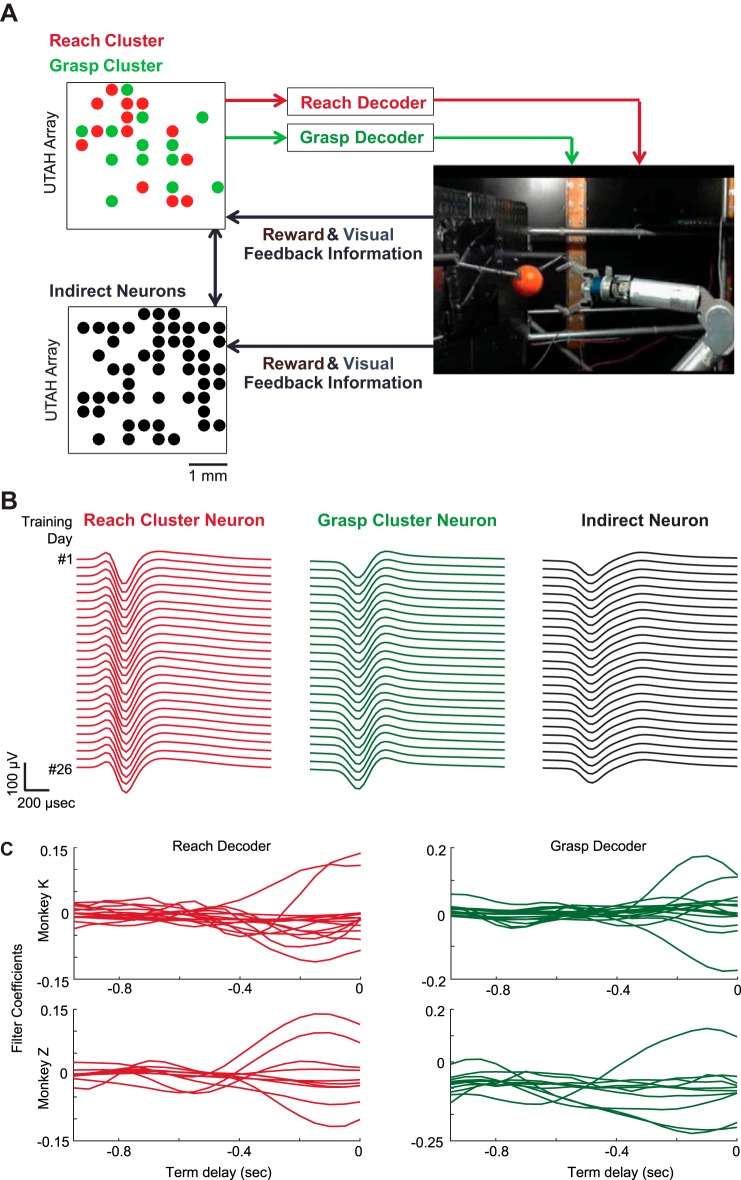
Fig. 1.
Experimental setup. A: the macaques were taught to use a neural cluster to reach (red) and grasp (green) with a robotic arm. Twenty-tap Wiener filter decoders were initialized using spontaneous data from each ensemble and remained static over the course of the study. The macaques learned this mapping such that they could coordinate both control dimensions to perform successful trials. Instruction was provided through operant conditioning (reward feedback). B: average daily waveforms of example neurons from a reach decoding cluster (red), grasp decoding cluster (green), and the pool of stable indirect neurons (black). C: filter coefficients of the 20-tap Wiener filter reach (red) and grasp (green) decoders for monkey K (top row) and monkey Z (bottom row).