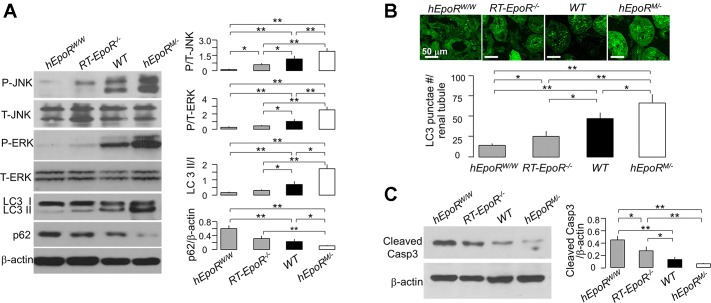
Fig. 9.
Association of EpoR signaling activity with levels of autophagy and apoptosis in the kidney. A: states of renal autophagy in mice with different EpoR (hEpoRW/W mice, RT-EpoR−/− mice, WT mice, and hEpoRM/− mice) signaling activity at baseline. Representative immunoblots for phospho-ERK, total ERK, phospho-JNK, total JNK, LC3, and p62 in the kidney (left) and a summary of all immunoblots (right panel). AKI was induced in hEpoRW/W mice, RT-EpoR−/− mice, WT mice, and hEpoRM/− mice by bilateral renal ischemia of 30 min followed by reperfusion for 48 h (IRI) for evaluation of autophagy (B) and of apoptosis (C). B: GFP-LC3 puncta per renal tubule. Representative micrographic images of LC3 puncta (top), scale bar = 50 μm; bottom: summary of the number of GFP-LC3 puncta per renal tubule from analysis of 50 renal tubules in the zone of cortex plus OM in blind manner. C: representative immunoblots for caspase 3 in the kidney of AKI mice (left) and summary of all immunoblots (right). Data are expressed as means ± SD from each group, statistical significance was evaluated by one-way ANOVA followed by Student-Newman-Keuls post hoc test, and significance was accepted when *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, between 2 groups.