Fig. 8.
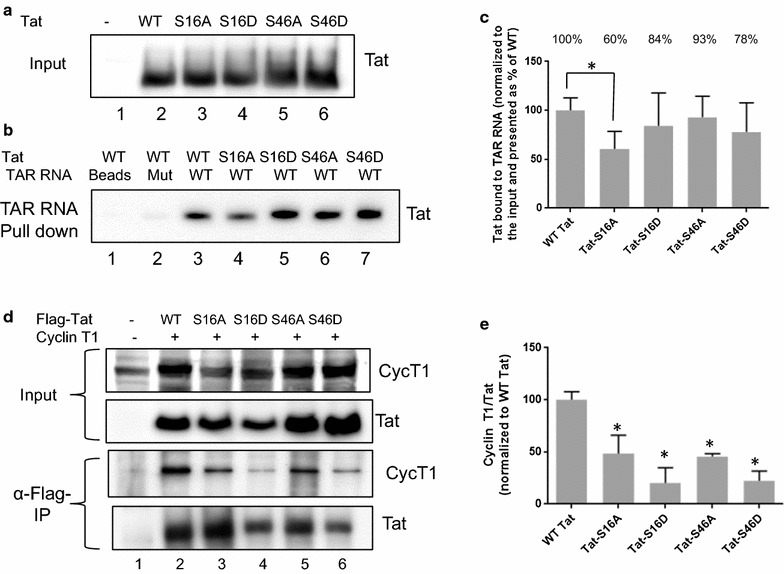
Effect of Tat S16A, S16D, S46A and S46D mutations on the interaction with TAR RNA and association with cyclin T1. a–c Tat Ser-16 and Ser-46 mutations decrease the interaction of Tat with TAR RNA. 293T cells were transfected with plasmids expressing WT Flag-Tat, Flag-Tat S16A or Flag-Tat S46A. The cells were lysed at 48 h posttransfection and the lysates were incubated with WT TAR RNA and mutant TAR RNA lacking bulge and immobilized on streptavidin beads. The beads were washed and proteins were eluted with SDS loading buffer and resolved on the 12% SDS-PAGE. Tat and TAR RNA were detected with anti-Flag and anti-biotin antibodies, respectively. a Tat loading control. Lane 1, control minus Tat. b Tat bound to the TAR RNA beads. Lane 1, control beads with no TAR RNA. Lane 2, control with mutant TAR RNA. c Quantification of Tat bound to TAR RNA beads relative to the loading control with asterisk indicating p ≤ 0.01. d, e Tat Ser-16 and Ser-46 mutations decreased Tat association with cyclin T1. 293T cells were transfected with plasmids expressing WT Flag-Tat, Flag-Tat S16A, Flag-Tat S16D, Flag-Tat S46A and Flag-Tat S46D and with cyclin T1 expressing vector. The cells were lysed at 48 h posttransfection. Tat was immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibodies from the lysates and proteins were resolved on the 12% SDS-PAGE. Tat and cyclin T1 were detected with anti-Flag and anti-cyclin T1 antibodies. e Quantification cyclin T1/Tat ratio adjusted to the WT Tat control. Mean of three independent measurements ± SD are shown.*p ≤ 0.001
