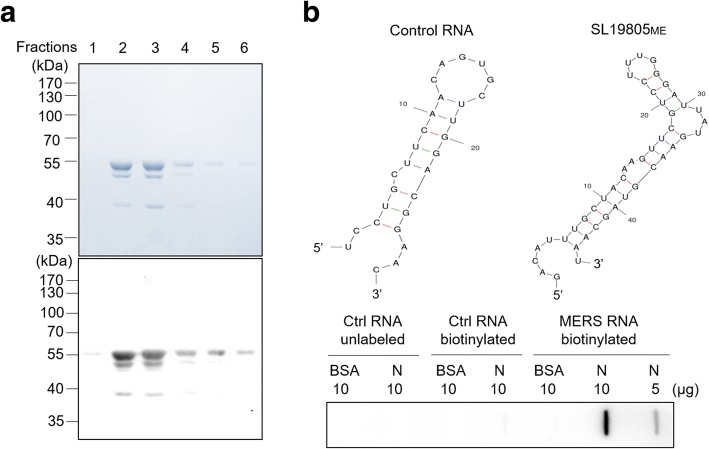
Fig. 4.
The RNA binding activity of MERS-CoV N protein. a Purification of the His-tagged MERS-CoV full-length N protein. Following expression of the His-tagged MERS-CoV N protein in E. coli BL21(DE3), the cells were lysed and cell supernatant collected was subjected to protein purification on a nickel-bead affinity column. The His-tagged MERS-CoV N protein eluted by a buffer containing 200 mM imidazole was detected by Coomassie blue staining (top) and Western blot analysis using antibody against the His-tag (bottom). Fractions 2 and 3 were pooled together for the filter binding assay. b Filter binding assay. The interactions between the MERS-CoV N protein and the biotin-SL19805ME probe were analyzed by the filter binding assay. Unlabeled and 3’ biotin-labeled RNA fragments with sequences 5′–UCCUGCUUCAACAGUGCUUGGACGGAAC–3′ and the predicted structure (as shown) were used as controls for RNA specificity. BSA was used as a protein control