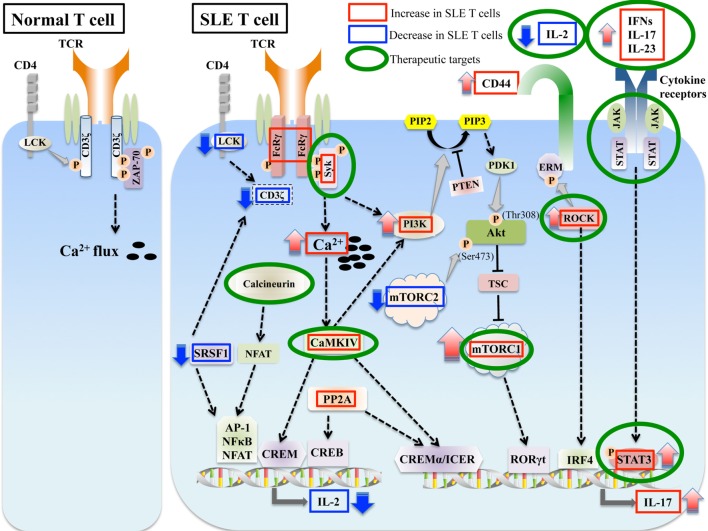
Figure 1.
Aberrant signaling in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) T cells. SLE T cells are characterized by multiple aberrant signaling pathways, such as decreased CD3ζ, activated PI3K-Akt-mTORC1 pathway, Rho associated protein kinase (ROCK), calcium/calmodulin kinase IV (CaMKIV), and protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A). These are associated with abnormalities in T cell differentiation and production of proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-17 and decreased production of vital cytokines such as IL-2. Molecules aberrantly increased or decreased in SLE are indicated in red and blue boxes, respectively, and molecules that are potential therapeutic targets are in green circles.