Fig. 1.
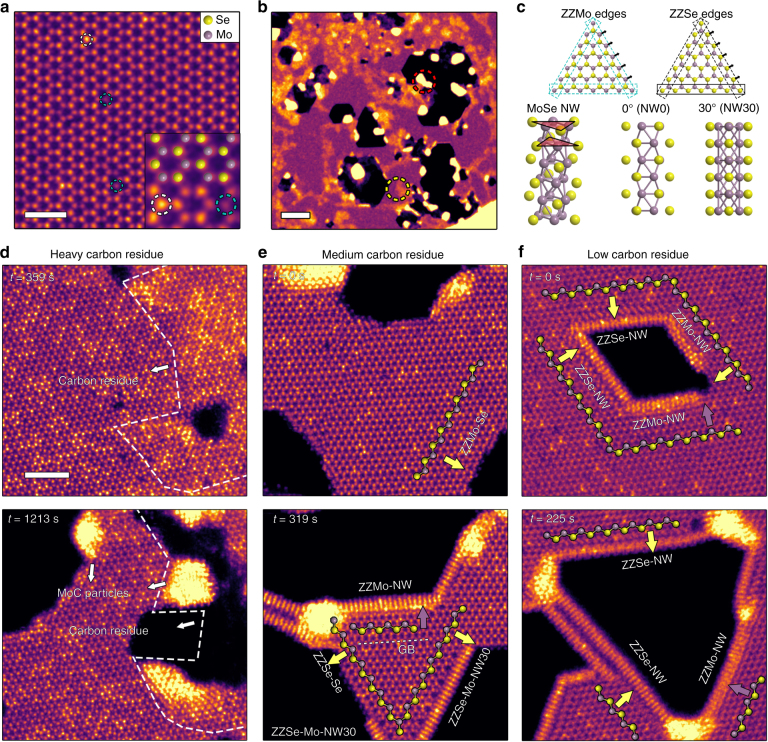
In situ heating and etching of monolayer Mo0.95W0.05Se2 with edge reconstructions. a Atomic resolution HAADF-STEM image showing the crystal structure of monolayer Mo0.95W0.05Se2. The white and cyan dashed circles indicate W dopants and Se vacancies, respectively. Inset: a structural model is overlaid on the HAADF-STEM image. Yellow, Se atoms; purple, Mo atoms. b Low magnification HAADF-STEM image of monolayer Mo0.95W0.05Se2 after in situ heating at 500 °C. The red dashed circle marks a MoC particle. The yellow dashed circle indicates carbon residue area with bright contrast. c (Top) atomic structure models of Mo-oriented ZZMo edges with Mo atoms pointing out normal to the edge (cyan dashed boxes) and Se-oriented ZZSe edges with Se atoms pointing out of the edge (black dashed boxes). (Bottom) atomic structure models of the MoSe NW formed on the edges and the two commonly-observed projections NW0 and NW30. d–f Atomic resolution HAADF-STEM images at initial and later stages of etching from areas with heavy (d), medium (e), low (f) carbon residue. Carbon residue and MoC nanoparticles are indicated by white arrows. ZZSe and ZZMo edges are indicated by white and purple arrows, respectively. Scale bars are 1 nm, 10 nm, and 2 nm for (a), (b), and (d), respectively