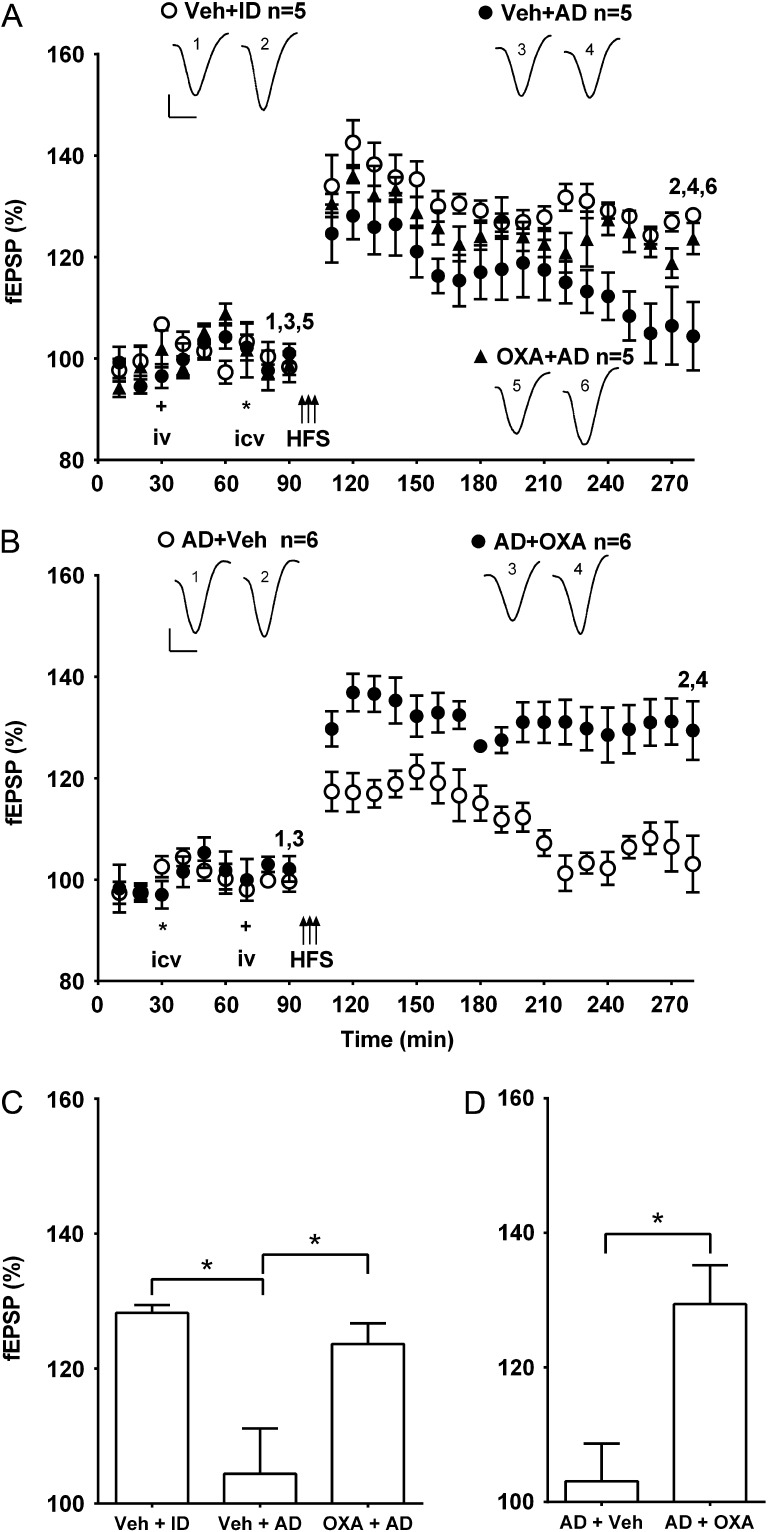
Figure 5.
Systemic pretreatment or posttreatment with oxaloacetate abrogates the inhibition of LTP by Aβ-containing AD brain extracts. (A,B) Time course graphs showing the effect of AD brain extracts on LTP in the presence of either (A) pretreatment or (B) posttreatment with oxaloacetate. (A) The magnitude of LTP was significantly reduced in animals injected with brain extract AD1 (AD, 6 µl i.c.v.) 20 min before HFS and 40 min after systemic vehicle (Veh + AD) (P > 0.05 compared with pre-HFS baseline at 3 h post-HFS). In contrast, the same extract that had been immunodepleted of Aβ (Veh + ID) had no effect on LTP (P < 0.05 compared with pre-HFS baseline). Importantly, in animals pretreated with oxaloacetate (35 mg/kg, i.v.) 40 min before AD (OXA + AD) the application of HFS 20 min later triggered stable LTP (P < 0.05 compared with pre-HFS baseline). (B) In animals pre-treated first i.c.v. (asterisk) with brain extract AD2 from a different patient (8 µl), and subsequently i.v. (plus symbol) with vehicle (AD + Veh), the application of HFS induced a decremental synaptic potentiation (P > 0.05 compared with pre-HFS baseline at 3 h post-HFS). In contrast, in animals injected with AD and subsequently treated with oxaloacetate (35 mg/kg, i.v.) (AD + OXA) the application of HFS 20 min later triggered stable LTP (P < 0.05 compared with pre-HFS baseline). Insets show representative fEPSP traces at the times indicated. Calibration bars: vertical, 1 mV; horizontal, 10 ms. (C,D) Summary bar charts comparing the magnitude of synaptic potentiation at 3 h post-HFS between groups (C) pre- and (D) post-treated with oxaloacetate. Values are the mean ± SEM fEPSP amplitude expressed as a percentage of the pre-HFS baseline. *P < 0.05.