Figure 10.
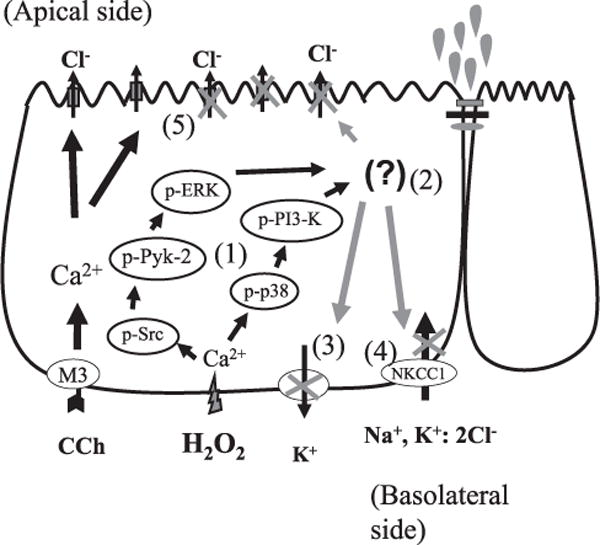
Integration of H2O2-activated regulatory signaling pathways. 1). H2O2 stimulates an increase in cytosolic Ca2+ concentration, which triggers two separate kinase pathways that are required for the overall inhibitory effect of H2O2 on Ca2+-dependent Cl− secretion. 2). Whether these pathways influence different downstream transport processes or converge via a downstream signal is unknown. 3). H2O2 also inhibits basolateral Ca2+-responsive K+ efflux. 4). H2O2 inhibits NKCC1 activity independently of possible effects on apical Cl− channels. 5). The inhibition of K+ efflux and NKCC1 activity likely contributes to the overall inhibitory effect of H2O2 on Ca2+-dependent ion transport in colonic epithelial cells.
