Figure 7.
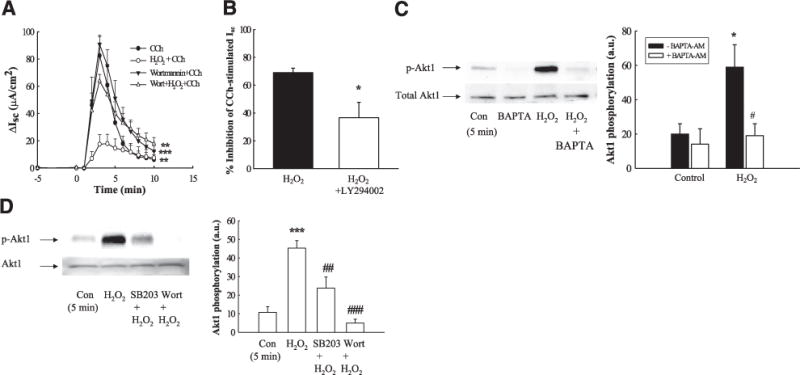
H2O2 inhibition of Isc involves PI3-K activation downstream of p38 activation. A) T84 monolayers mounted in Ussing chambers were treated with the PI3-K inhibitor, wortmannin (50 nM), for 30 min prior to addition of H2O2, and subsequent Isc responses to CCh (100 μM) were measured (n=4). B) T84 monolayers mounted in Ussing chambers were treated with the PI3-K inhibitor, LY294002 (20 μM), for 30 min prior to addition of H2O2, and subsequent Isc responses to CCh (100 μM) were measured (n=4). Data are expressed as percentage inhibition of CCh-stimulated Isc response. C) Monolayers were pretreated with BAPTA-AM (20 μM; 30 min) prior to incubation with H2O2 (500 μM; 5 min). Lysates were blotted for phosphorylation of the downstream PI3-K target, Akt1 (T308; n=4). D) T84 monolayers were preincubated for 30 min with the p38 inhibitor, SB203580 (10 μM; n=5), or the PI3-K inhibitor, wortmannin (50 nM; 30 min; n=5), and H2O2-stimulated Akt1 phosphorylation was measured. Results are means ± SE for phosphorylation (a.u., arbitrary units). *P<0.05; ***P<0.001 vs. H2O2 + CCh (A, B) or control (untreated cells; C, D). #P<0.05; ##P<0.01; ###P<0.001 vs. cells treated with H2O2 alone.
