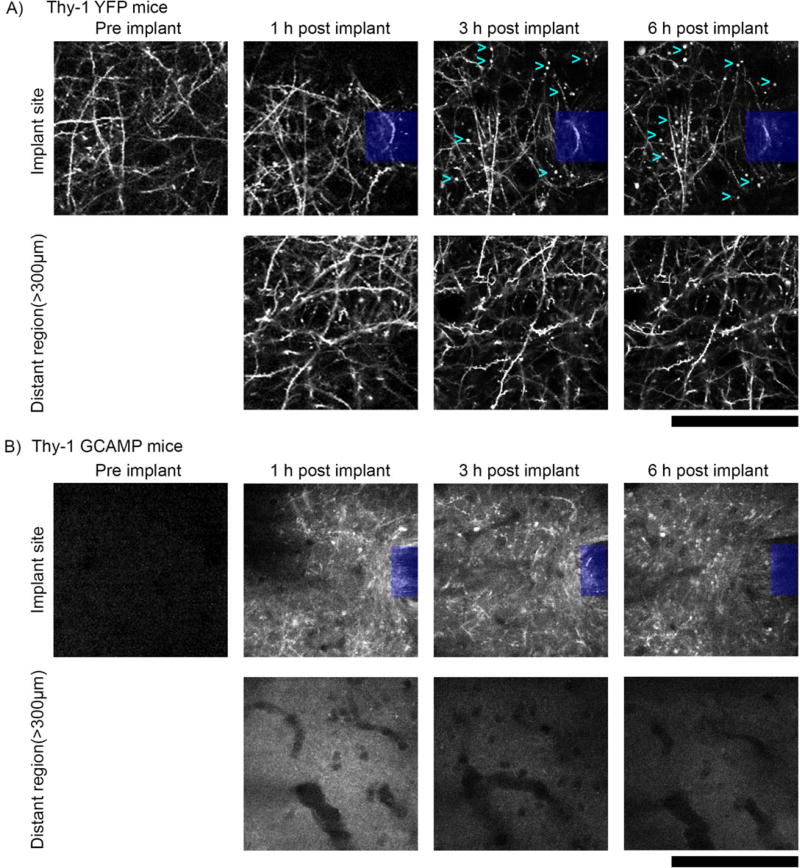
Figure 12. Axonal protrusions/blebs form by 3h post-implant at the implantation site, but not apparent in distant regions (> 300µm from implant).
a) Top: 2-photon microscopy of the visual cortex of transgenic mice expressing YFP in neurons under the control of the Thy1 promoter (n=3) reveal axonal dysfunction in the vicinity of silicon implants (denoted by blue box) by 3h post–implant. Axonal protrusions (examples denoted by cyan >) display as bright spherical objects, typically 1–5µm in diameter. Bottom: Axons in distant regions (> 300µm from implant) have clear axonal cable morphology, with spines clearly visible perpendicular to neurites and no signs of protrusions. b) Top: Neuronal Ca++ activity reporter mice (Thy-1 GCAMP, n=5) show similar axonal distress to Thy-1 YFP reporter mice. Compared to the same region prior to implant, axons from 1–6h post implant are brightly labeled with GCAMP, indicating sustained Ca++ influx. Bottom: Comparatively, distant regions (> 300µm from implant) do not show any discernable GCAMP(+) axons. All images, depth of imaging: between 0–50 µm. All scale bars are 100 µm.