Fig. 3.
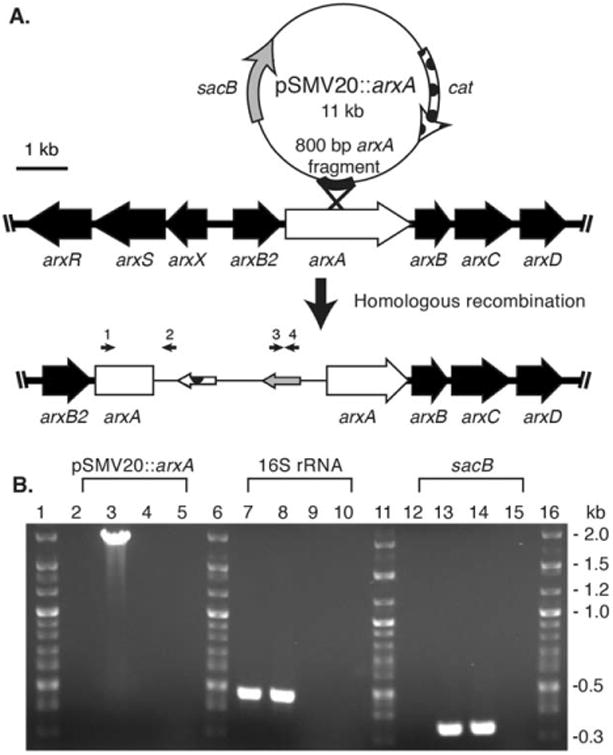
Development and verification of arxA disruption mutation in Ectothiorhodospira sp. str. BSL-9. (A) The pSMV20 vector was inserted within arxA via homologous recombination. (B) PCR analysis for DNA from wild-type BLS-9 (2, 7, 12), ARXA1 (3, 8, 13), empty pSMV20 vector (4, 9, 14), and water (5, 10, 15). The following PCR primers were used: (i) arxA (Ext_arxA_F, arrow 1) gene and vector-specific (M13_R, arrow 2) (lanes 2-5), (ii) 16S rRNA (0341_16SV3V4-F and 0785_16SV3V4-R) gene (lanes 7-10) and (iii) sacB (sacB_F and sacB_R, arrows 3 and 4) (lanes 12-15). PCRs were analysed by agarose (1%) gel electrophoresis.
