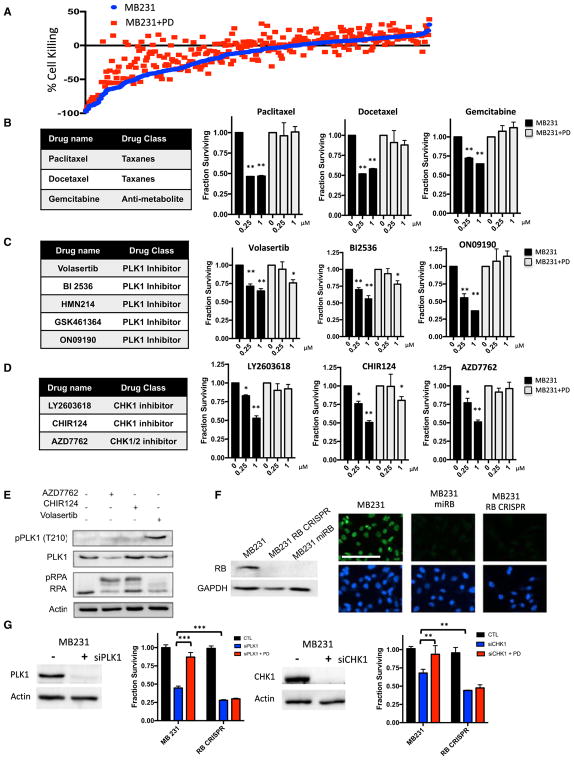
Figure 2. CDK4/6 Inhibition Selectively Inhibits Sensitivity to Cell-Cycle Active Agents.
(A) Sensitivities of agents within the SelleckChem chemical library are defined as individual dots. The sensitivity in the presence (red) or absence (blue) of CDK4/6 inhibitor palbociclib (PD) is plotted.
(B) Dose-response relationship between naive and palbociclib-pretreated MB231 cultures with the indicated chemotherapy agents. The mean and SD are shown (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, as determined by t test).
(C) Dose-response relationship between naive and palbociclib-pretreated MB231 cultures with the indicated PLK1 inhibitors. The mean and SD are shown (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, as determined by t test).
(D) Dose-response relationship between naive and palbociclib pretreated MB231 cultures with the indicated CHK inhibitors. The mean and SD are shown (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, as determined by t test).
(E) Immunoblot analysis of the indicated proteins from MB231 cells treated with the CHK (AZD7762 and CHIR124) and PLK1 inhibitors.
(F) Immunoblot analysis of RB-proficient and deficient models developed with a synthetic miRNA (miRB) or CRISPR/CAS9 mediated deletion. Immunofluorescence was used to confirm that less than 1% of the cells contained detectable nuclear RB staining (scale bar, 100 μm).
(G) Knockdown of PLK1 and CHK1 was performed in either RB-positive or RB-deficient cell populations by RNAi transfection. The efficacy of the knockdown was confirmed by immunoblot analysis of PLK1 and CHK1 in MB231 cells. Treatment with palbociclib was protective only in cell lines that contain RB, and RB-deficient models were more sensitive to the depletion of CHK1 and PLK1. The mean and SD are shown (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, as determined by t test).