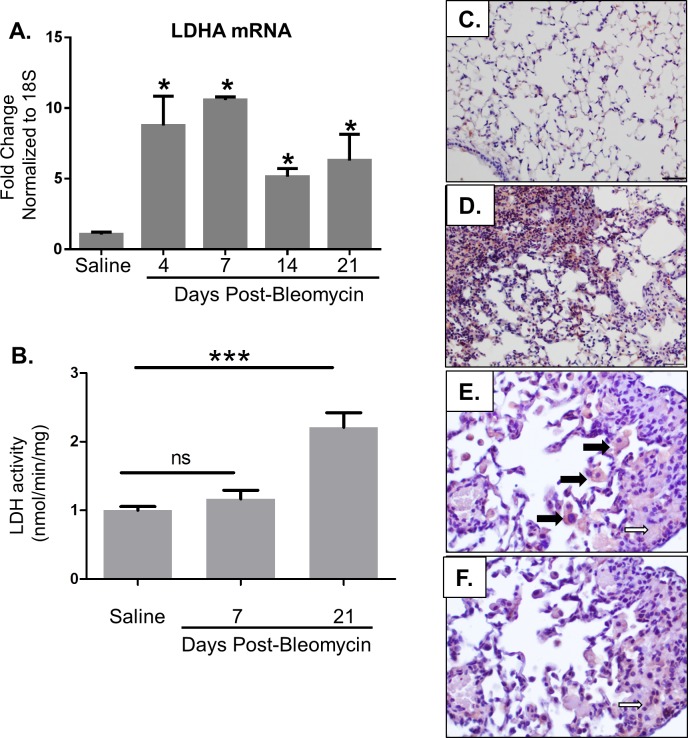
Fig 1. LDHA is increased in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis.
Mice were exposed to saline or bleomycin via oropharyngeal aspiration (OA) and euthanized at indicated time points. (A) Total RNA was isolated from the right lung lobes and qRT-PCR was performed to measure LDHA mRNA. Data are displayed as fold change from saline controls normalized to 18S. *p≤0.05 compared to saline controls by t-test. n = 4–5 per group. (B) LDH activity was measured on lung tissue homogenates in mice administered either saline or bleomycin. ***p<0.001. (C-D) Lung tissue from mice at day 21 post bleomycin was stained for LDHA by immuno-histochemistry in red. Images were taken at 20X magnification, scale bars represent 50 μm. (E-F) Serial section immunohistochemistry was performed for LDH shown in panel E and αSMA shown in panel F. Images were taken at 40X magnification. LDHA expression localized to both macrophages (bold arrows) and areas co-staining for αSMA (open arrows), a marker of myofibroblast differentiation.