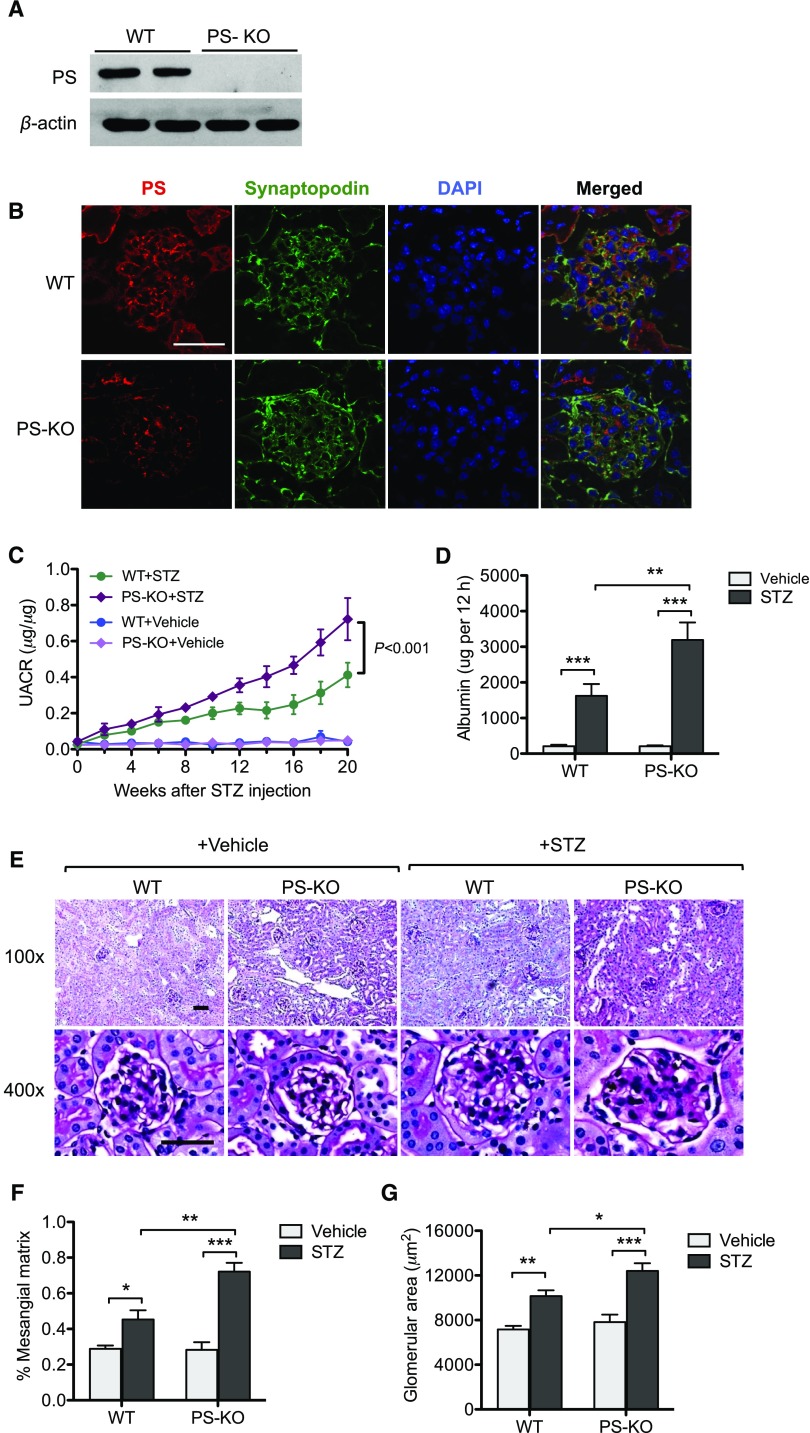
Figure 6.
Diabetic glomerulopathy is aggravated in PS-KO mice. (A) Western blot analysis of PS in the lysates of primary podocytes isolated from PS-KO and control WT mice. (B) Immunostaining of PS and synaptopodin in the kidney shows loss of PS specifically in podocytes in PS-KO mice. (C) Urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio is shown over the course of 20 weeks post–diabetes onset. (D) The 12-hour urinary albumin excretion rate was determined at 20 weeks post–diabetes onset. (E) Representative images of periodic acid–Schiff–stained kidneys of vehicle- or STZ-injected WT and PS-KO at both low (×200) and high (×400) magnification. (F and G) Quantification of (F) glomerular area and (G) percentage of mesangial matrix area are shown (60 glomeruli per group; n=6; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, and ***P<0.001 when compared between indicated groups). DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; PS-KO+Vehicle, PS-KO injected vehicle control; WT+Vehicle, WT injected with vehicle control; PS-KO+STZ, PS-KO injected with STZ; WT+STZ, WT injected with STZ; UACR, urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio.