Fig. 3.
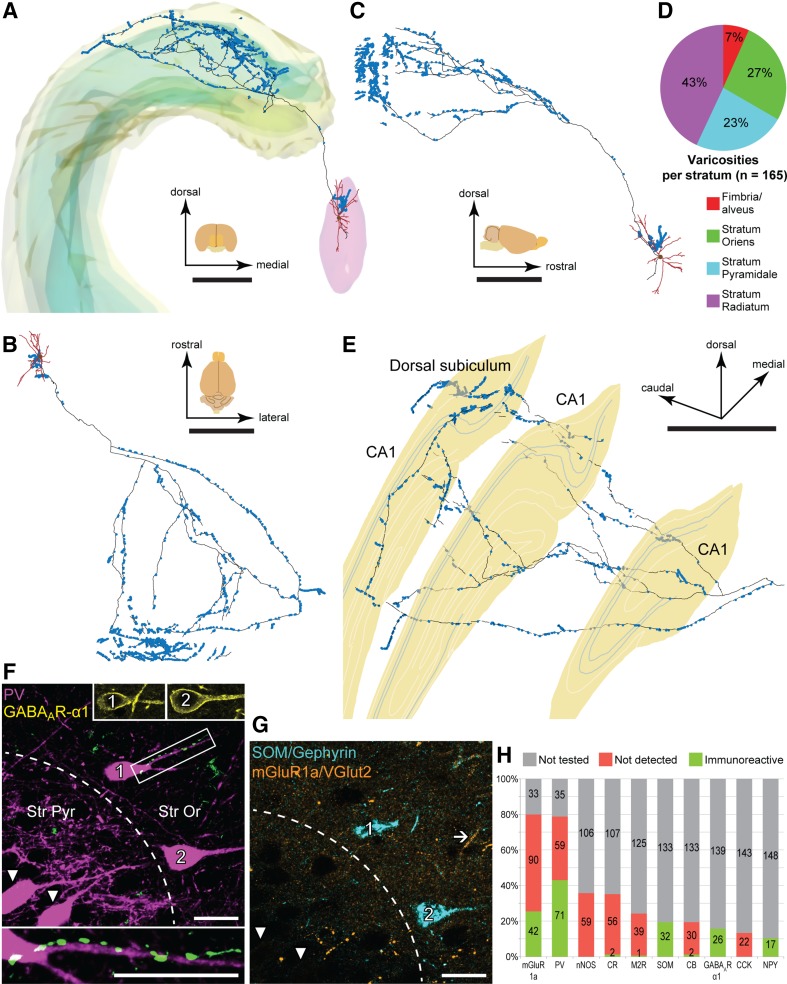
Projection patterns and targets of theta-coupled GABAergic medial septal neuron D55c. a–c Digital reconstruction of the neuron in frontal (a), top (b) and side (c) views showing the soma and dendrites (brown) in the MS (pink, a) and the axon (black) bearing varicosities (blue). Parts of the axon lost in 2 sub-optimally processed sections appear as gaps. The frontal view includes the contours of the pyramidal and granular layers (green) in the hippocampus (yellow, a). d Laminar distribution of axonal varicosities in CA1 tested for postsynaptic molecular cell markers. e Reconstruction of the axon after its first branching point at an oblique angle shows innervation of the CA1 and dorsal subiculum. Three single sections (yellow) are represented along the axon. Blue contours mark borders of stratum pyramidale. f, g Two bistratified cells (1, 2) in stratum oriens of the CA1 are immunoreactive for PV (f), GABAAR-α1 (f, upper insets) and SOM (g), but lack detectable immunoreactivity for mGluR1a (g; arrow, an immunopositive profile). The soma and a proximal dendrite of bistratified cell 1 are in apposition to septal boutons (green; framed area in f, enlarged in the inset below). Two other PV-immunopositive, SOM/mGluR1a-negative neurons in stratum pyramidale (arrowheads, f, g) were not observed to be contacted by the septal axon. h Normalized distribution of immunoreactivity for each tested molecule in presumed postsynaptic targets of septal boutons (n = 165, numbers within columns). Many axonal targets were tested for several molecules in sequential reactions. Individual targets were contacted by 1–16 boutons. f, g Maximum intensity projections of confocal image stacks; 2.93 µm-thick. Median filter was applied (x, y, z: radius 1 pixel) in f, g. Scale bars, 1 mm in a–e, 20 µm in f, g. Scale bar in F applies to the small insets