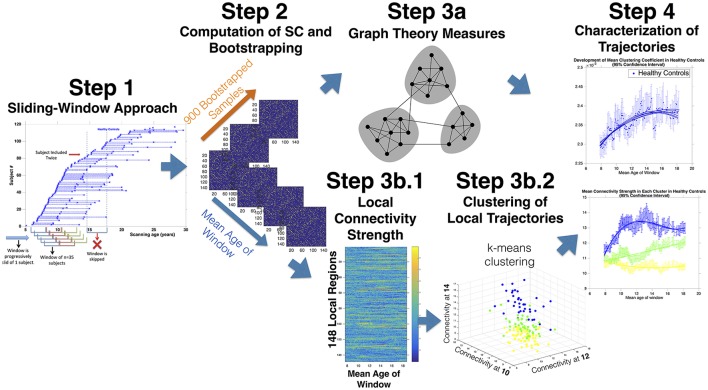
Figure 1.
Sliding-Window Methodological Protocol: Step 1: Scans are ordered according to age. Subsequently a window of 35 subjects is progressively slid across the cohort starting for the 35 youngest scans at advancing by of one scan at a time. The procedure yields partially overlapping age-windows of progressively increasing mean age. Step 2: Covariance matrices are computed in each partially overlapping age-window. Subsequently scans included in each age-window are resampled for 900 leave-one-out substitution bootstrapped samples (BSs). Step 3a: The global architecture of covariance matrices computed in each age-window and each BS are characterized with Graph Theory measures, obtaining a distribution of each measure at each age-window. Step 3b.1: Local connectivity strength is computed for each region and each age-window yielding a matrix of regions by age. Step 3b.2: K-means clustering is then employed to identify clusters of regions showing common maturation. Connectivity strength is averaged within each cluster at each age-window. Step 4: Models of increasing order are fit to measures of SC and BIC are employed to select model order. The process is repeated for 900 BSs to define confidence intervals of developmental trajectories.