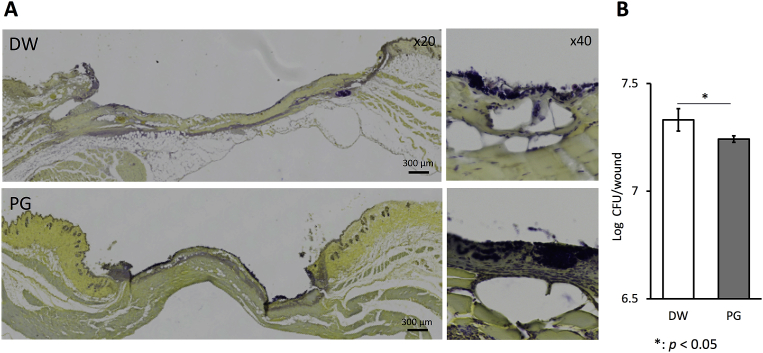
Fig. 2.
Effect of PG on S. aureus infection in wound. Mice were inoculated with 20 μL of 2.5 × 109 CFU/mL of S. aureus at the sites of skin wound immediately after wounding, and then treated with 10 μL of 10 mg/mL PG daily. On day 2, the skin tissues were collected and paraffin sections were prepared. The sections were stained with crystal violet, Lugol's iodine solution and picric acid (A). Bacterial cells (dark blue) localized on yellow background of mouse tissue. The bacterial number of homogenates of whole wounds was determined (B). The data are representative (A) and the results are expressed as the means ± SD of 2 independent experiments (5 mice per group per each experiment) (b). An asterisk (p < 0.05) indicates that the value is significantly different from the DW control group.