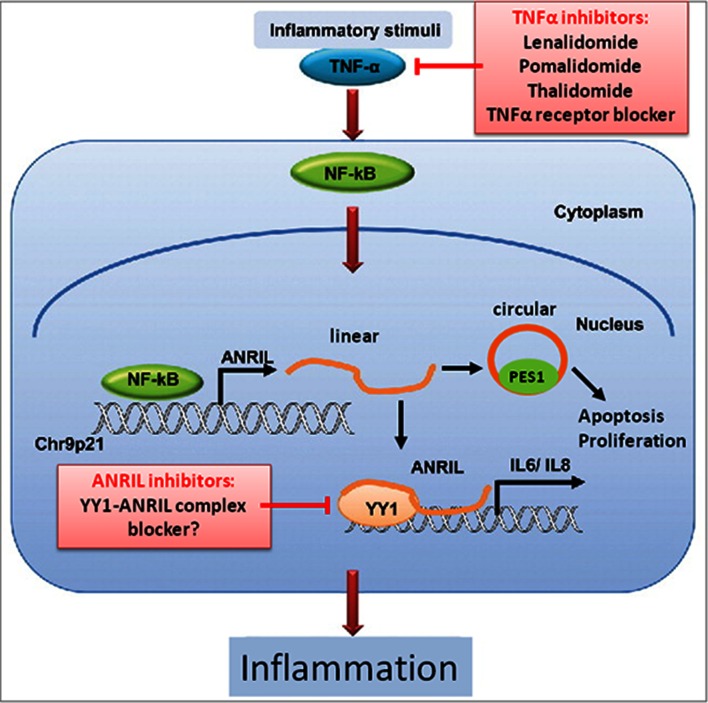
Figure 1.
Hypothetical roles of linear and circular ANRIL lncRNA in regulating inflammation and cell survival in human vascular endothelial cells and potential drug targets. TNF-α triggers NF-κB activation, which induces ANRIL transcription (66). Linear ANRIL can be converted to circular ANRIL (38). Linear ANRIL interacts with the transcription factor yin yang-1 (YY1) to form a functional complex that binds to and regulates expression of target genes such as IL-6/8. Circular ANRIL interacts with pescadillo homologue 1 (PES1) to form a complex with the pre-ribosomal assembly complex, that impairs ribosome biogenesis, leading to activation of p53 and a subsequent increase in apoptosis and decrease in the proliferative rate (41). This pathway may promote atheroprotection by eliminating over-proliferating cells in atherosclerotic plaques. Neither TNFα nor NF-κB antagonists do seem suitable for wide-spread use in anti-inflammatory therapies of PD or CAD, because of their serious side effects. Since ANRIL is located downstream of TNFα and NF-κB, ANRIL or its downstream targets may be better suited as drug targets to inhibit the pro-inflammatory activities linked to this signaling pathway [modified according to ref. (78)].