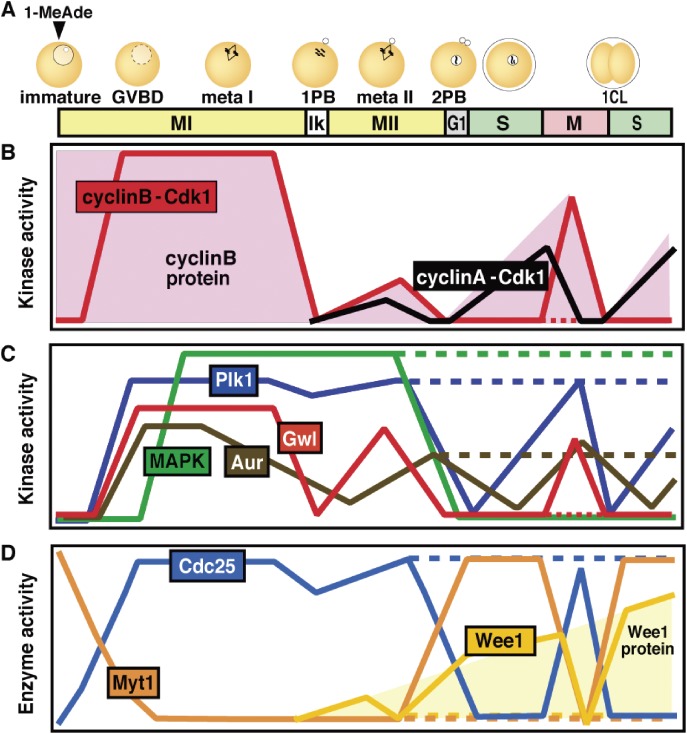
Figure 3.
Dynamics of cell cycle regulators and their choreographers in starfish meiotic and early cleavage cycles. (A) Fully grown immature starfish oocytes are arrested at prophase of meiosis I (MI), which is equivalent to G2-phase in somatic cells. This arrest is characterized by the presence of a large nucleus called the germinal vesicle (GV). Once these immature oocytes are isolated into seawater and treated with 1-MeAde (1-methyladenine), the starfish maturation-inducing hormone, meiosis resumes as hallmarked by GV breakdown (GVBD), followed by two consecutive M-phases, MI and meiosis II (MII), without an intervening S-phase. After the completion of MII, mature haploid eggs arrest at G1-phase unless fertilization occurs. Starfish oocytes are fertilizable throughout the meiotic cell cycle (even at prophase I or G1-phase), whereas physiological fertilization possibly occurs in late MI. After the completion of MII, fertilized eggs start to undergo cleavage cycles consisting of alternating S- and M-phases. The cell cycle dynamics of various regulators are schematically shown in B–D. meta I and meta II, metaphase of MI and MII, respectively; Ik, interkinesis period; 1PB and 2PB, the first and second polar body; 1CL, the first cleavage. (B) Cyclin B protein is already present in immature oocytes. By contrast, cyclin A protein (and Wee1 protein shown in D) is undetectable in immature oocytes and starts to accumulate near the end of MI (shaded areas). After meiotic resumption, the protein levels of cyclins A and B cycle along with the cell cycle, peaking at each metaphase. The Cdk1 level remains constant throughout the entire process. Accordingly, Cdk1 activity is represented by cyclin B-Cdk1 in MI, and largely by both cyclin B-Cdk1 and cyclin A-Cdk1 in and after MII. (C, D) In contrast to cyclins, the protein levels of Cdc25, Myt1, Greatwall kinase (Gwl), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1), and Aurora (Aur) remain constant throughout the entire process. All of Gwl, Plk1, Aur, and MAPK are activated downstream of cyclin B-Cdk1 at meiotic resumption. The meiotic cycles are characterized by the unique dynamics in activities of MAPK and Plk1, and hence Cdc25 and Myt1 during the MI to MII transition and after the completion of MII (during G1-phase arrest) in unfertilized eggs (dotted lines). In contrast, Gwl activity correlates with cyclin B-Cdk1 activity. PP2A-B55 and PP1 activities are assumed to roughly mirror those of cyclin B-Cdk1 and Gwl. See the text for details.