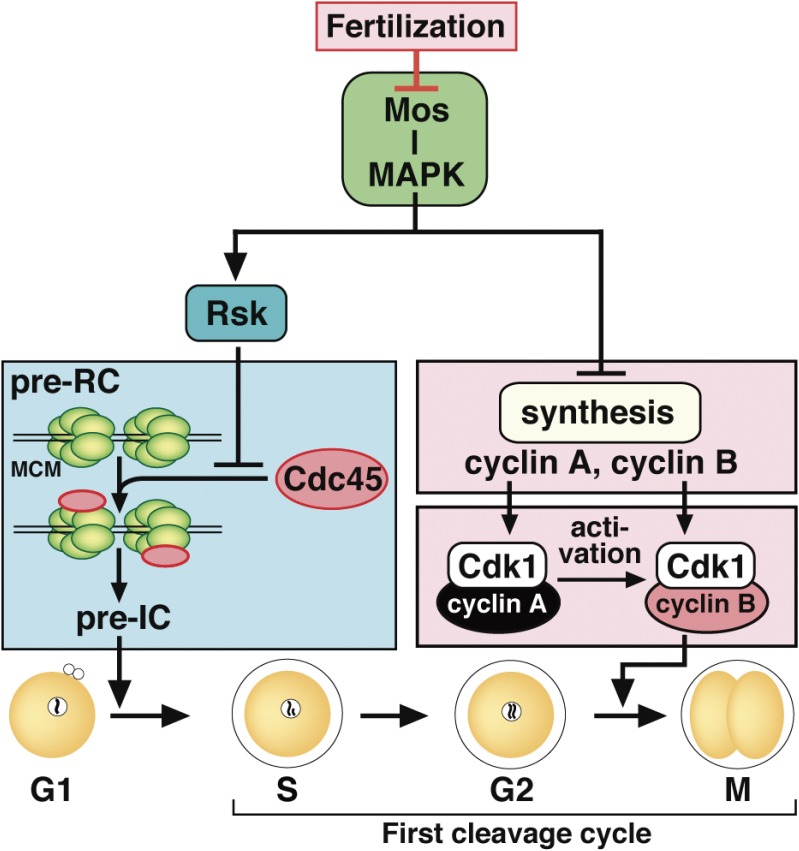
Figure 6.
Dual-lock for G1-phase arrest in unfertilized mature starfish eggs. Unless fertilized, mature starfish eggs arrest at G1-phase after the completion of meiosis II. This arrest is accomplished through two separate pathways that function downstream of Mos–MAPK signaling. One is a Rsk-mediated pathway that prevents entry into S-phase by inhibiting Cdc45 loading onto the DNA replication machinery. The initiation of DNA replication is thus blocked by Rsk at the pre-replicative complex (pre-RC) stage, prior to the subsequent pre-initiation complex (pre-IC) stage just before the actual start of DNA replication. The other is an Rsk-unmediated pathway that prevents entry into the first mitotic M-phase by inhibiting new protein synthesis of cyclin A and cyclin B. Due to the absence of a DNA replication checkpoint, this dual-lock mechanism is required for G1 arrest. Upon fertilization, Mos degradation releases the dual-lock, resulting in the start of the embryonic mitotic cycle. MCM, MCM complex.