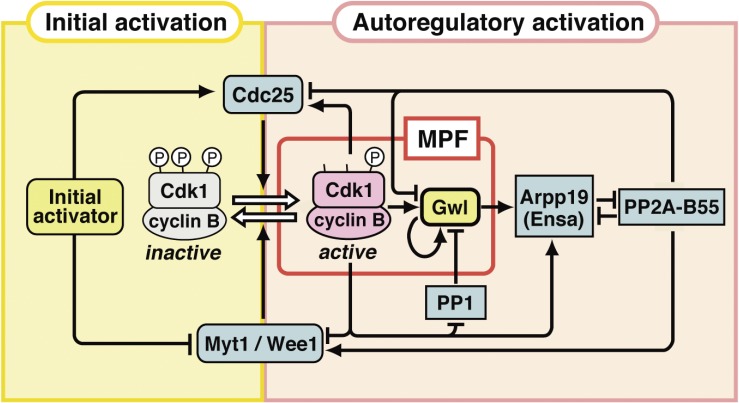
Figure 9.
Molecular pathway for autoregulatory activation of cyclin B-Cdk1, and its core kinases, cyclin B-Cdk1 and Gwl, that constitute MPF. The autoactivation loop consists of two kinases, cyclin B-Cdk1 and Gwl, that promote activation of cyclin B-Cdk1, and two phosphatases, PP2A-B55 and PP1, that counteract activation of these two kinases. Once cyclin B-Cdk1 is initially activated, it causes, on one hand, suppression of the major antagonizing phosphatase PP2A-B55 via Arpp19 in two steps: First, direct phosphorylation of Arpp19 by initially activated cyclin B-Cdk1 converts Arpp19 into an inhibitor of PP2A-B55, and subsequent phosphorylation of Arpp19 on another residue by Gwl, which is activated downstream of cyclin B-Cdk1, enhances this conversion. On the other hand, initially activated cyclin B-Cdk1 directly phosphorylates and inhibits phosphatase PP1 which antagonizes the autoactivation of Gwl. Collectively, the cyclin B-Cdk1–Arpp19 pathway and the cyclin B-Cdk1–Gwl–Arpp19/Ensa pathway synergistically inhibit PP2A-B55 to support phosphorylation of Cdc25 and Myt1/Wee1 by cyclin B-Cdk1, resulting in the autoregulatory activation of cyclin B-Cdk1. The authentic, classical MPF is the system (composed of cyclin B-Cdk1 and Gwl) that initiates and accomplishes the autoregulatory activation of cyclin B-Cdk1 under intracellular circumstances in which the initial activation of cyclin B-Cdk1 is not allowed. Gwl contributes to MPF by accelerating the suppression of PP2A-B55 that counteracts the autoregulatory activation of cyclin B-Cdk1. Reproduced from Fig. 6 in Ref. 13 with some updates.