FIGURE 7.
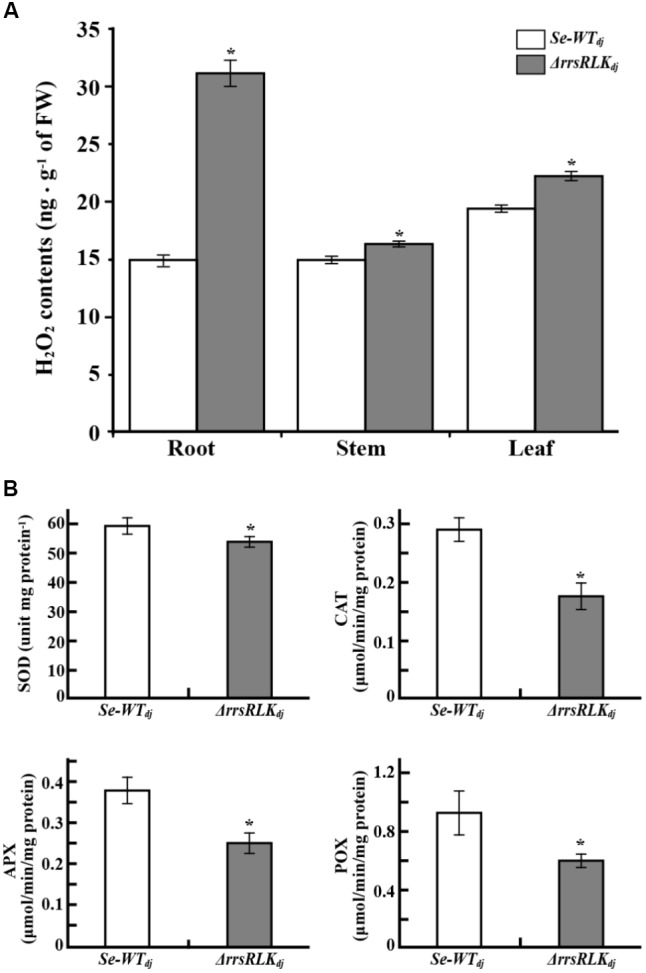
(A) H2O2 content in tissues of SE-WTdj and ΔrrsRLKdj. Content of H2O2 in 1 g of tissue (root, stem, and leaf) of SE-WTdj and ΔrrsRLKdj was spectrophotometrically determined at 436 nm by the modified method of Bernt and Bergmeyer (1974) using peroxidase enzyme. (B) Activity assay of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), ascorbate peroxidase (APX), and peroxidase (POX) in leaves of SE-WTdj and ΔrrsRLKdj. Total protein was extracted from 1 g of leaves from SE-WTdj and ΔrrsRLKdj rice, and the activity of ROS-scavenging enzymes was spectrophotometrically monitored at A560nm (SOD), A240nm (CAT), A290nm (APX), and A436nm (POX) using a modified method of Beyer and Fridovich (Beyer and Fridovich, 1987). All assays were repeated more than three times, and the error bars of each sample denote the mean ± SD (n = 9). The asterisks indicate that a significant difference (P < 0.05) in the H2O2 was detected between transgenic plants and wild type.
