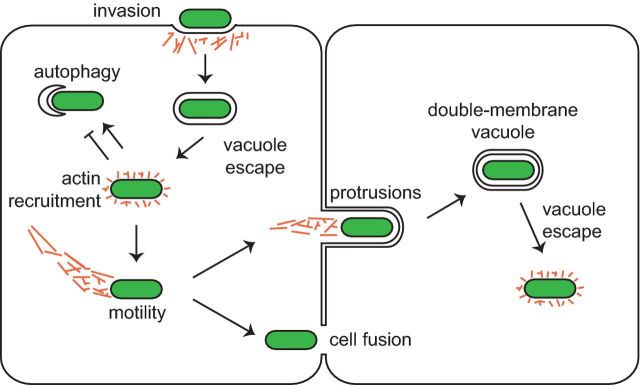
Figure 1.
Actin assembly and ABM play several roles in infection. Actin (orange) is mobilized during multiple stages of infection by intracellular pathogens (green). Actin facilitates bacterial invasion of the host cell. For bacterial pathogens that escape the vacuole into the cytosol, the recruitment of actin and/or actin-interacting proteins on the bacterial surface can influence its susceptibility to autophagy. Moreover, actin assembly powers bacterial ABM through the host cytosol, enabling bacteria to reach the cell periphery, where they enter into protrusions that are engulfed by neighboring cells or promote cell–cell fusion.