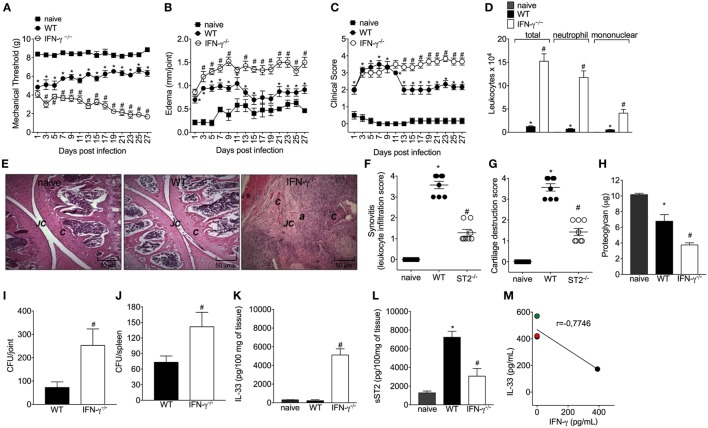
Figure 6.
Interferon-γ (IFN-γ) contributes to the resolution of staphylococcal arthritis. Staphylococcus aureus or saline was injected in in the femur-tibial joint of wild-type (WT) and IFN-γ−/− mice. (A) Mechanical hyperalgesia, (B) articular edema, and (C) clinical score were evaluated over 27 days post-infection. At 28-day post-infection, knee joint samples were collected at 28-day post-infection to determine: (D) leukocyte recruitment to the articular cavity, histopathological analysis of hematoxylin/eosin stained slices: (E) representative images of knee joints at 28 post-infection in original magnification ×10. The letter a indicates a heavily inflamed joint with cartilage destruction and pannus formation, (F) synovitis score (intensity: 1–4), and (G) cartilage destruction score (intensity: 1–4). At 28-day post-infection, (H) proteoglycan content in patellas, (I) bacterial counts in knee joint cavity, (J) and were determined, and (K) interleukin-33 (IL-33) and (L) sST2 concentrations in knee joints were determined by ELISA. Correlation analysis of IL-33 and IFN-γ levels determined by ELISA in synovial fluid samples from patients with septic arthritis. For inflammatory parameters and proteoglycan content: n = 6 per group per in vivo experiment, representative of two independent experiments. *P < 0.05 vs naïve mice group, #P < 0.05 vs WT mice group (A–D,H–L). One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test. For histological analysis: n = 8 per group per experiment, representative of two independent experiments. *P < 0.05 vs naïve mice group, #P < 0.05 vs WT mice group (E–G). Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s test. Spearman rank correlation test was used for the assessment of correlation (M). Abbreviations: C, cartilage; JC, joint cavity.