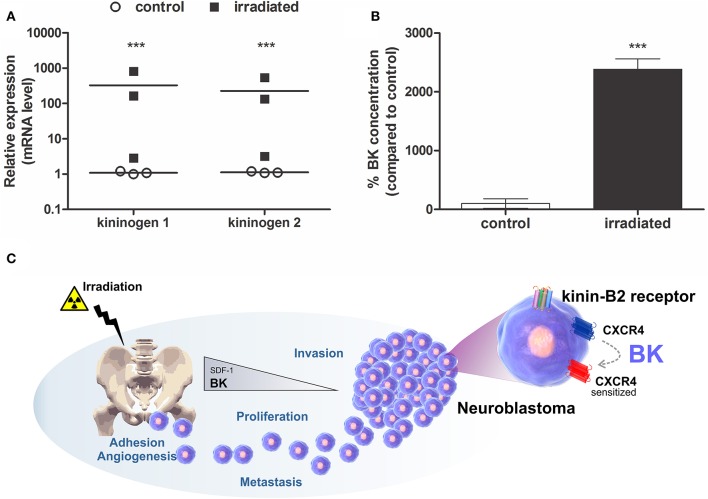
Figure 1.
Expression of Bradykinin in Bone Marrow. BK concentration and it precursor RNA level were determined in murine bone marrow lysates prepared from the animal 24 h after irradiation (1,000 cGy). (A) mRNA levels of kininogen 1 and kininogen 2. Measurements were performed for samples from three independent isolations. Each analysis was performed in triplicates. (B) BK levels in bone marrow of irradiated mice compared to non-irradiated mice (control). The data are shown as mean of six independent experiments and plotted as percentages compared to the control (100%). ***p <0.001 compared to control. (C) Mechanistic illustration of BK-promoted neuroblastoma metastasis. BK levels increase in the bone marrow of animals that received radiation, a situation mimicking radiotherapy during cancer treatment. In this case, the levels of SDF-1, the main chemo-attractor of hematopoietic stem cells to the bone marrow, is reduced. However, BK as priming agent sensitizes the SDF-1 receptor (CXCR4), also expressed by neuroblastoma cells, induces expression of metalloproteinase (MMP-2 and/or MMP-9) important for tumor invasion and VEGF, a key protein in the mechanism of angiogenesis, and enhances adhesion and proliferation of neuroblastoma cells.