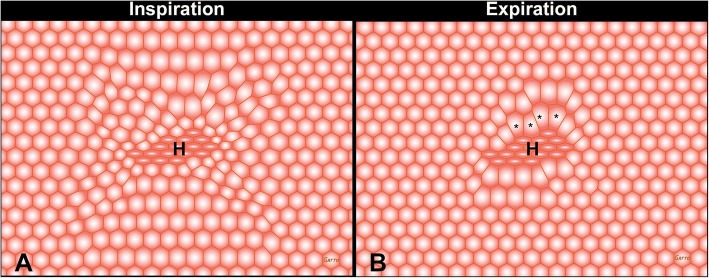
Fig. 5.
Interdependent “alveoli” with shared walls represented by hexagons at inspiration and expiration. In the center of the “alveolar tissue” there are a group of heterogeneously (H) collapsed alveoli causing a stress-riser. Since alveoli share walls, the open alveoli connected to collapsed alveoli are subject to a concentration of the force applied to lung tissue by the tidal volume. Note that the over-distension and distortion are most significant in alveoli surrounding H during expiration (asterisks). Stress-risers are a key mechanism of ventilator-induced lung injury [8]