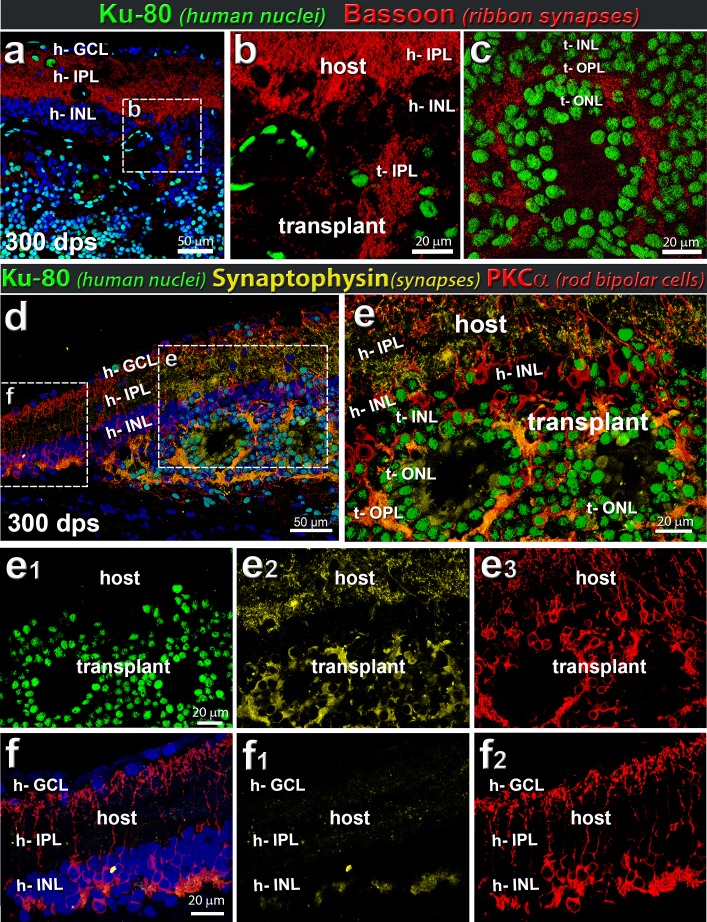
Figure 7.
Rat host and human retinal transplant synaptic markers. Example of transplant at 300 dps. (a–c) Combination of Bassoon (red, indicative of ribbon synapses) and Ku80 (human nuclei, green) (n = 5). (a, b) Ribbon synapses (bassoon; red) are found in the host bipolar cells demarcating host IPL. (a–c) Ribbon synapses can be seen within the transplant (Ku80; green) and surrounding rosettes. The donor bipolar cells generate a bassoon-staining IPL (t-IPL) (b) and donor photoreceptors create a bassoon-immunoreactive OPL (t-OPL) (c). (d–f) Combination of synaptophysin (yellow), PKCα (red), and Ku80 (green). Within transplant (example at 300 dps), Ku80+ PKCα+ cells express high levels of synaptophysin, as would be expected of functioning human neurons. (d) Overview image of transplant. € Enlargement of transplant/host interface. The ONL surrounding the photoreceptor rosettes highly expresses synaptophysin, indicative of functional neurons and connectivity. Note the extensive synaptophysin immunoreactivity (yellow) in the IPL of the host retina (e, e2). Single channels are shown in (e1) Ku80 (green), (e2) synaptophysin (yellow), and (e3) PKCα (red). (f) Enlargement of host retina adjacent to transplant, containing no Ku80+ transplant cells. Single channels (f1) synaptophysin (yellow), and (f2) PKCα (red). Note that there is significantly less synaptophysin immunoreactivity in the IPL in this area (f1) compared to the host IPL overlying the transplant (e2). (a, d, f) Nuclei are stained blue with DAPI (n = 5).