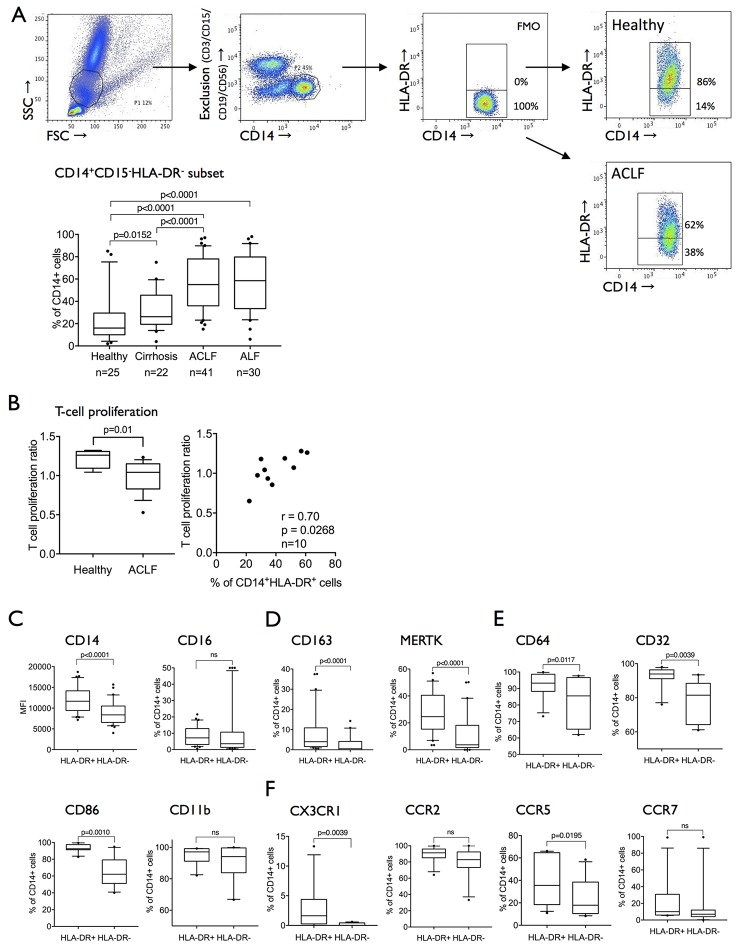
Figure 1.
The expanded CD14+CD15−HLA-DR− population in ACLF is attributed to the previously defined monocytic MDSC subset. (A) Gating strategy to determine CD14+CD15−HLA-DR− cells: whole blood was sorted, monocytic cells were selected, and non-monocytic cells were excluded by lineage gating (CD3, CD15, CD19, CD56). CD14+, lineage negative cells were divided into HLA-DR+ and HLA-DR- subsets using FMO. Prevalences of the CD14+CD15−HLA-DR− populations in healthy subjects, patients with cirrhosis, ACLF and ALF. (B) T cell proliferation in a mixed lymphocyte reaction assay is significantly reduced in ACLF and in relation to HLA-DR expression on monocytes in coculture (healthy n=2, ACLF n=8). (C–F). A large panel of myeloid cell differentiation markers was compared between the CD14+HLA-DR+ and CD14+HLA-DR− populations. The CD14+HLA-DR− monocytic subset appears to be CD14+CD15−CD11b+HLA-DR−CD64+ in line with the previously defined monocytic MDSC (M-MDSC). (C) Classical markers of monocyte differentiation were reduced in M-MDSC (CD14, CD163, MERTK). (D) FCγ receptors (CD64, CD32) were abundantly expressed in M-MDSC but lower in comparison to CD14+HLA-DR+ cells (n=30) and (E) markers of monocyte activation (CD86, CD11b) were reduced or equally expressed in M-MDSC. (F) Selected chemokine receptor expression (CX3CR1, CCR5) was lower in the M-MDSC population (n=11). Data are expressed as MFI and % of CD14+ cells and shown as box plots; Wilcoxon tests. ACLF, acute-on-chronic liver failure; ALF, acute liver failure; FMO, fluorescence minus one control; FSC, forward scatter; MDSC, myeloid-derived suppressor cells; MERTK, Mer Tyrosine Kinase; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity; SSC, side scatter.