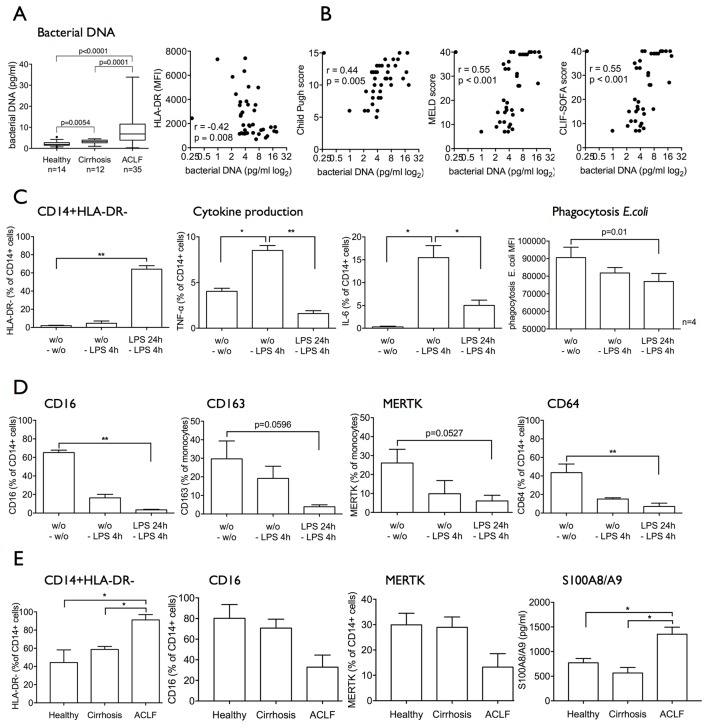
Figure 5.
Circulating bacterial products and cytokines in patients with ACLF may lead to the generation of an immunosuppressive M-MDSC-like population. (A) Bacterial DNA levels in whole blood were significantly elevated in patients with ACLF and negatively correlated with HLA-DR expression. (B) Accordingly, bacterial DNA levels in whole blood positively correlated with markers of disease severity (Child-Pugh, MELD, CLIF-SOFA). (C and D) Healthy CD14+ cells were incubated with TLR-4 ligand LPS for 24 hours and subsequent 4 hours (n=4 independent experiments). HLA-DR expression, cytokine responses to LPS, phagocytosis capacity (C) and phenotype (CD16, CD163, MERTK, CD64, TLR-4, TLR-3, TLR-9) (D) were assessed. Recurrent LPS stimulation leads to the generation of an immunosuppressive HLA-DRlowCD16lowCD163lowMERTKlow M-MDSC-like population. Data are presented as % of CD14+ cells or MFI, respectively. Paired t-tests. (E) ACLF plasma containing bacterial products and modulated cytokine levels led to generation of an HLA-DRlowCD16lowMERTKlow M-MDSC-like population. S100A8/A9 protein secretion into the supernatants response to LPS was significantly increased. Plasma from n=3 healthy subjects, n=3 cirrhotics, n=6 ACLF, Mann-Whitney U tests. ACLF, acute-on-chronic liver failure; CLIF, Consortium on Chronic Liver Failure; IL-6, interleukin-6; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; MELD, Model for End-Stage Liver Disease; MERTK, Mer Tyrosine Kinase; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity; M-MDSC, monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells; SOFA, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score; TLR-4, Toll-like receptor 4; TNF-α, tumour necrosis factor-alpha.