Figure 2.
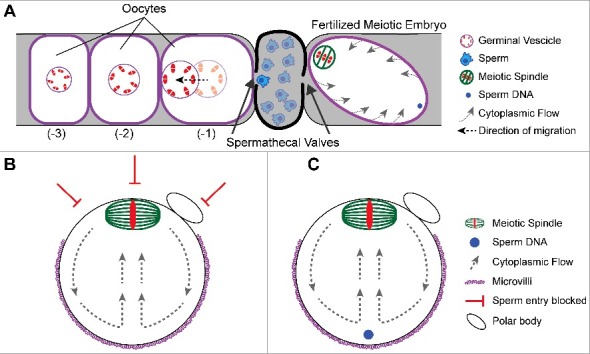
Mechanisms governing sperm entry site. (A) Schematic of a C. elegans germline depicting the spatial separation of oocytes from sperm. Oocytes mature and increase in volume as they become closer to the spermatheca. Once an oocyte becomes the -1 oocyte, the germinal vesicle migrates to the cortex away from the spermatheca. The sperm will fertilize at the cortex closest to the spermathecal valve as it dilates. The sperm is on the opposite side of the meiotic spindle. Despite the cytoplasmic flows around the embryo, the sperm stays at that position. (B) Schematic of a metaphase II mouse oocyte. The meiotic spindle is positioned at the cortex by cytoplasmic flows. The cortical localization of the meiotic spindle prevents microvilli formation and sperm entry. (B) Schematic of a fertilized metaphase II mouse embryo depicting the sperm underlying the microvilli during cytoplasmic streaming.
