Figure 2.
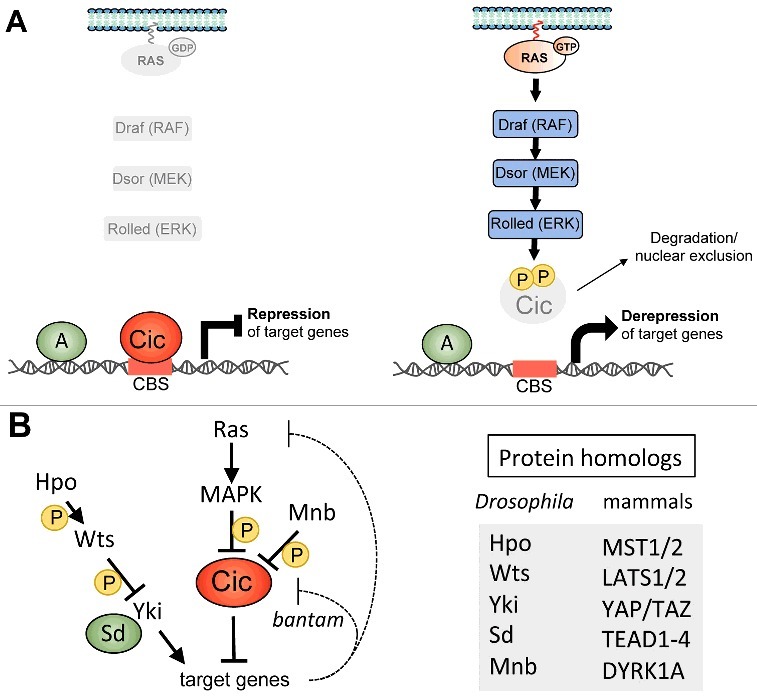
Role of Cic in Ras-MAPK signaling and growth control. (A) Regulation of Cic repressor activity via MAPK signaling in Drosophila. In the absence of RTK/RAS/MAPK signaling, Cic acts as a default repressor by binding to specific Cic-binding sites (CBS) in its target genes (left). Upon RTK activation, RAS proteins become GTP-bound and initiate a phosphorylation cascade via the kinases Draf (RAF ortholog), Dsor (MEK ortholog) and the MAPK Rolled (ERK ortholog) causing phosphorylation of Cic, which in turn results in its degradation and/or nuclear exclusion (right). As a consequence, Cic target genes are transcriptionally induced (derepressed) at specific times and places during development. This induction depends on transcriptional activators (A) which remain only partially characterized. Two confirmed activators of Cic targets are Dorsal and Zelda, which activate the intermediate neuroblasts defective gene in the early embryo [7,12,13]. Zelda also appears to activate tailless, [14] another embryonic Cic target [1,12,15]. See also panel B and [2] and [11]. (B) Summary of Cic regulatory interactions in Drosophila growth control. In addition to its role downstream of Ras signaling, Cic mediates cross-interactions with the Hippo (Hpo) pathway and other regulatory inputs. For example, both Cic and the Sd:Yki co-activator complex regulate a common set of target genes, which become induced upon simultaneous reduction of Hpo signaling (leading to Sd:Yki upregulation) and Cic repressor activity. Some of these targets, including the Ets transcription factor Pnt [8,11] and the bantam microRNA, [10,16,71,72] are directly controlled by both Cic and Sd/Yki, whereas the input of Sd:Yki on other targets appears to be indirect, possibly via JAK/STAT signaling [11]. This latter set of targets includes negative feedback regulators of Ras signaling such as Argos and Sprouty, whose activity is represented by a dashed loop. bantam has also been proposed to function in a negative feedback loop to downregulate Cic expression levels. Finally, recent evidence linking Mnb kinase activity to both Cic [18] and Hpo signaling [19] (not included in the model) implies the existence of additional layers of crosstalk. Cic and Sd are DNA binding proteins and are represented by ovals. The correspondence between Drosophila proteins illustrated in the diagram and their mammalian orthologs is indicated on the right. See main text for further details.
