Figure 3. Responding to centrosome defects.
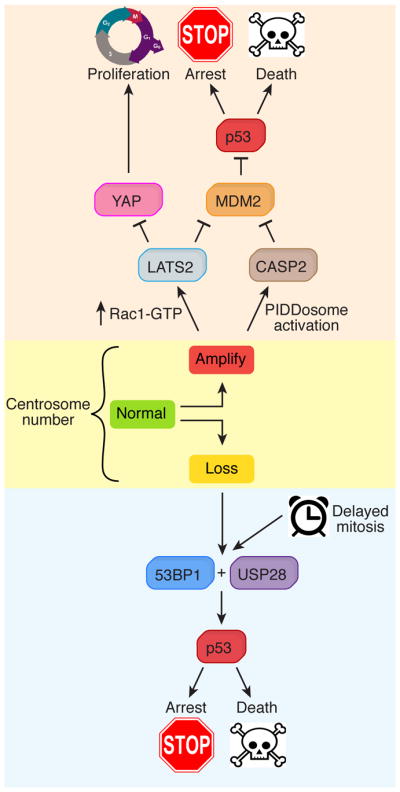
Pathways activated by centrosome loss (bottom) and centrosome amplification (top). Centrosome loss leads to 53BP1 and USP28-dependent stabilization of p53, which in turn promotes either cell death or cell cycle arrest133,136–138. An increased duration of mitosis also activates p53 through the same pathway. Centrosome amplification leads to hyper-activation of Rac1 and a corresponding decline in RhoA-GTP. RhoA-GTP activates the LATS2 kinase, which stabilizes p53 through inhibition of MDM2. In addition, LATS2 phosphorylates and inactivates the transcription factor YAP to inhibit proliferation148. In an alternative pathway, supernumerary centrosomes promote activation of the PIDDosome, which leads to activation of Caspase-2149. Active Caspase-2 cleaves MDM2 and thereby stabilizes p53208.
