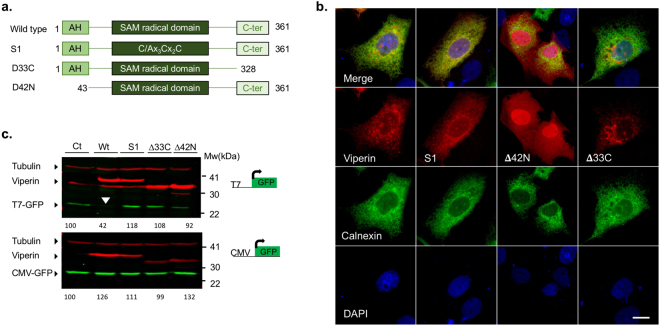
Figure 2.
Mutations in the functional domains of viperin abolish its effect on T7-GFP expression. (a) Schematic representation of the viperin mutants used. (b) Subcellular Localization of the viperin mutants. Viperin mutants were co-transfected into Huh7 cells with a plasmid expressing calnexin-GFP as an ER marker. The cells were fixed 24 h post transfection and immunostained using a viperin antibody. (c) Western blot showing the effect of the various mutants on T7-GFP or CMV-GFP expression. HEK293-T7 cells were co-transfected with wild type viperin or the viperin mutants Δ42 N, Δ33 C and S1 and T7-GFP or CMV-GFP. The cells were lysed and analyzed by Western blot with GFP (green) and viperin (red) specific antibodies 24 h post-transfection. Tubulin (red, top) was used as a loading control. The effect of wild type viperin is marked with a white arrow head. Quantification of the bands compared to luciferase control is shown at the top of each panel. Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. 2.