Fig. 3.
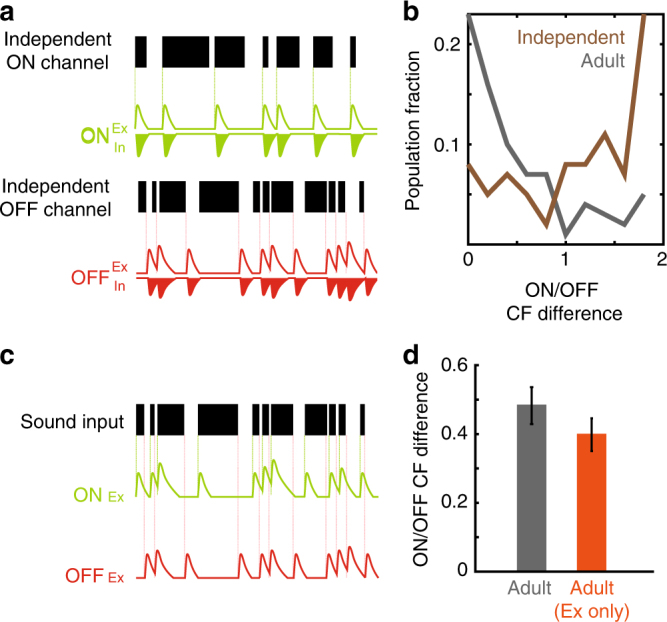
Determinants of ON/OFF RF divergence in silico. a Input scheme to investigate role of sound alternation in RF divergence. In contrast to Fig. 2 (trained with input sequences where ON and OFF always followed each other), the network is presented with independent ON and OFF sequences where ON/OFF inputs need not necessarily alternate. b Final distribution of ON/OFF CF differences for neurons (n = 100) trained with independent ON/OFF input sequences (brown). Adult population trained with natural alternating inputs shown for comparison (grey). c Input scheme to investigate role of fast evoked synaptic inhibition in RF divergence. Neurons receive evoked synaptic activity, driven by a sound sequence (black) that randomly switches ON (green dashed lines) and OFF (red dashed lines). Excitatory ON (green) and OFF inputs are evoked by sound onsets. Inhibitory inputs are omitted from the model. d Final mean difference between ON and OFF CF (n = 100 cells) in excitation-only model (Ex only, orange). Adult excitation-inhibition results shown for comparison (grey)
