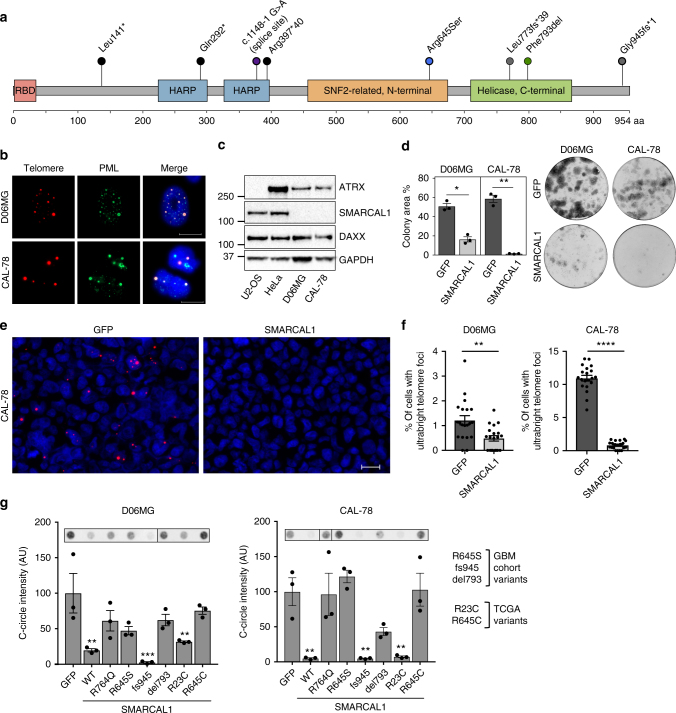
Fig. 4.
Inactivating mutations in SMARCAL1 mutations cause hallmarks of ALT. a The majority of mutations identified in SMARCAL1 in an expanded cohort (N = 39) of TERTpWT-IDHWT GBMs are likely inactivating (frameshift, nonsense). Protein domains of SMARCAL1 are shown (RBD RPA-binding domain, HARP HepA-related protein). b We identified two cancer cell lines harboring inactivating mutations in SMARCAL1: D06MG (patient-derived GBM, W479X) and CAL-78 (chondrosarcoma, deletion of exons 1–4). These cell lines exhibit signs of ALT, including ALT-associated PML bodies (APBs), as indicated by the co-localization of PML (immunofluorescence) and ultrabright telomere foci (FISH), and the accumulation of C-circles. c Western blot confirms the absence of SMARCAL1 expression in both CAL-78 and D06MG, as well as intact expression of ATRX and DAXX. Controls include U2-OS (ATRX-negative) and HeLa (positive control). d Overexpression of SMARCAL1 significantly decreased (D06MG, P < 0.05; CAL-78, P < 0.005) colony-forming ability as measured by percent area. e, f Overexpression of SMARCAL1 dramatically reduces the appearance of ALT-associated ultrabright telomere foci relative to the GFP control (CAL-78 is shown). g SMARCAL1 constructs harboring either wildtype, helicase dead (R764Q, from SIOD), mutations from the expanded cohort (R645S, del793, fs945) and recurrent mutations seen in pan-cancer data (R23C, R645C) were assayed for effects on ALT-associated C-circles. The SMARCAL1 helicase domain function is critical for suppression of C-circles, as constructs with mutations in these domains fail to fully suppress markers of ALT, compared to wildtype constructs or SMARCAL1 with mutations in the RPA-binding domain (R23C) or the 945 fs variant. Error bars in d, f, g denote s.e.m. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; Paired t-test (d, f) and one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test (g). Scale bar indicates 20 μm. Colony formation and C-circle experiments were performed in triplicate