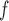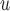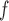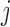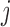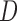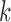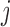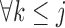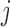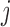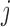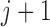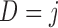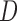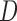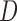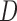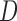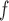IPW
|
u-MAR (1) u-MAR is equivalent to mortal-cohort dDTIC and missingness-independent death (2) u-MAR is the discrete death-time version of MAR in Kurland and Heagerty (2005) |
Model probability of dropout at visit 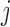 for those who survived up to visit for those who survived up to visit 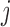 Do not include 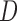 in dropout models in dropout models Appropriate when longitudinal and survival processes depend on one another, and survival process does not depend on dropout process u-MAR assumption can be tested if survival is known up to the end of study
|
IPW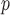
|
p-MAR Note: p-MAR is a weaker assumption than u-MAR |
|
IPW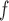
|
f-MAR (1) f-MAR is a weaker assumption than u-MAR (2) f-MAR is the discrete death-time version of MAR-S in Kurland and Heagerty (2005) |
|
MI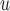 /LI /LI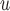
|
mortal-cohort dDTIC and independent death |
Do not include 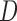 in the imputation models in the imputation models Delete imputed post-death outcomes before analysis Appropriate when survival and dropout processes depend on one another, and survival process does not depend on missing outcome process
|
MI /LI /LI
|
f-MAR |
|
AIPW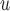
|
either i) u-MAR or ii) p-MAR, f-MAR and independent death |
Do not include 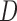 in dropout and imputation models in dropout and imputation models Delete imputed post-death outcomes At least as efficient as IPW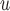 if dropout and imputation models are correctly specified and survival process does not depend on longitudinal process (death still truncates longitudinal and dropout processes) if dropout and imputation models are correctly specified and survival process does not depend on longitudinal process (death still truncates longitudinal and dropout processes)
|
AIPW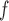
|
f-MAR |
Valid as long as either dropout or imputation models are correctly specified Include 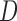 in dropout and imputation models in dropout and imputation models Delete imputed post-death outcomes At least as efficient as IPW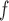 if dropout and imputation models are correctly specified and data are f-MAR if dropout and imputation models are correctly specified and data are f-MAR
|
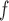
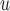 /LI
/LI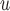
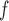 /LI
/LI