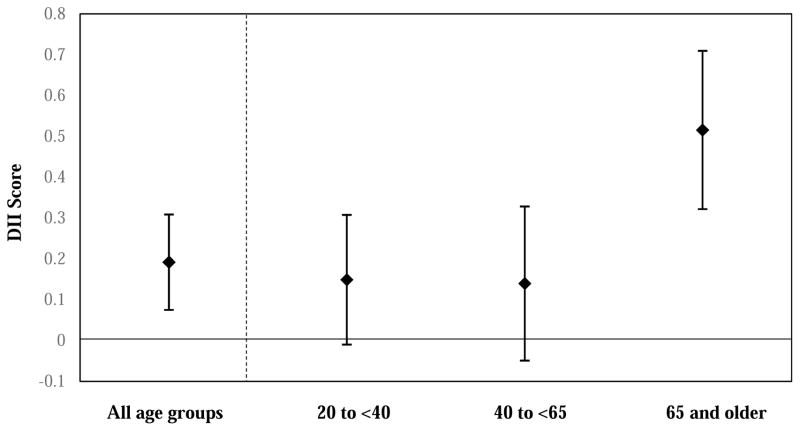
Figure 1.
The association between food insecuritya and DIIb score among lower-incomec adults and moderation by age groupd, e
aThose that reported marginal to very low food security were considered food insecure. Those that reported high food security were considered food secure.
bDietary Inflammatory Index
cAdults with an income-to-poverty ratio ≤3.00
dAdjusted for sex, race/ethnicity (non-Hispanic White, non-Hispanic Black, Hispanic, other), education (<high school, high school degree or equivalent, Associates degree or some college, collage and above), marital status (married or living with partner; separated, widowed, or divorced; never married), income-to-poverty ratio, employment status (employed, not working and not looking for work, not working and looking for work), health insurance status (private, subsidized, uninsured), and perceived health status (excellent or very good, good, fair or poor).
eThe p-value for the interaction between food insecurity and age group was 0.0103.