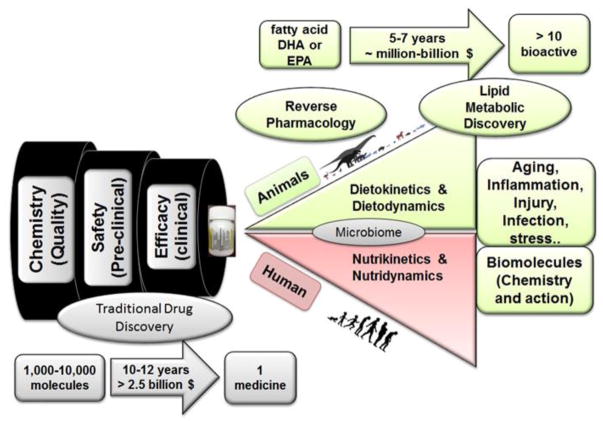
Figure 1. Process for Fatty Acid Drug Discovery (FADD) approach.
Illustration depicts the processes of traditional versus reverse pharmacology. Using fatty acids as drug biosynthesizing candidates, reverse pharmacology is a feasible, more cost-effective method to develop novel molecules to combat diseases associated with conditions such as aging, inflammation, injury, and infection. eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA); docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)