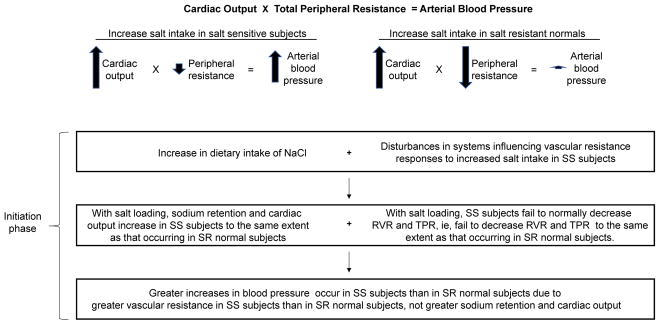
Figure 3. The vasodysfunction framework for the usual pathogenesis of salt-induced increases in blood pressure.
According to this conceptual framework, initiation of salt-induced hypertension (the acute phase) is hemodynamically mediated by an abnormal vascular resistance response to increases in salt intake, together with normal salt-induced increases in cardiac output.
RVR, renal vascular resistance; SS, salt sensitive; SR, salt resistant; TPR, total peripheral resistance.
Adapted from Kurtz et al. [36], with permission.