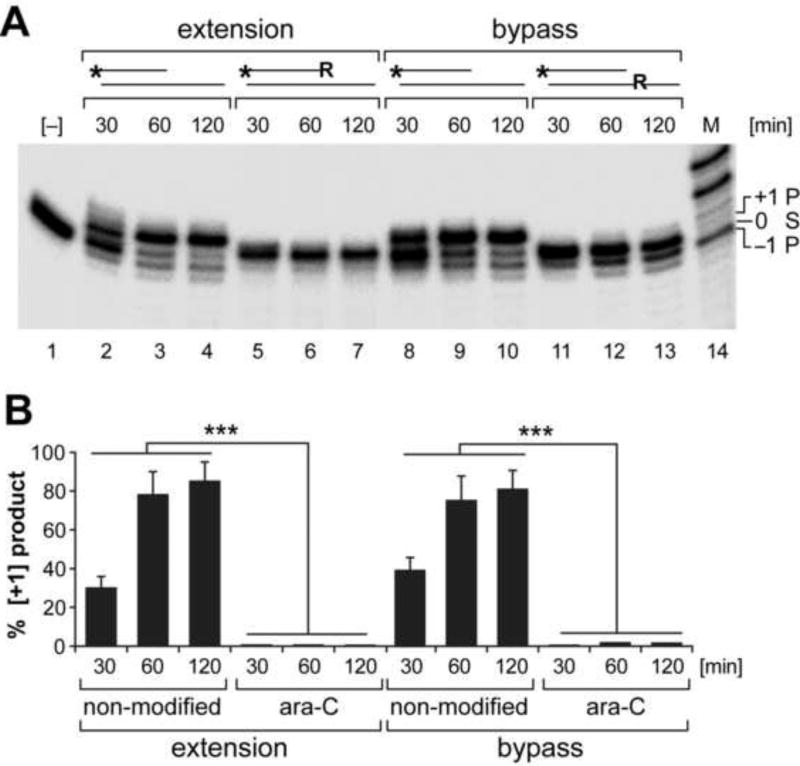
Figure 1. mtDNA polymerase γ activity is inhibited by the cytosine analog ara-C.
Reactions were assembled with end-labeled oligonucleotide substrates, dGTP and recombinant pol γ. (A) Substrate design is shown above the relevant lanes; * indicates 5’-end label; R - indicates ara-C residue. The one nucleotide extension [+1] product generated on non-modified substrate [lanes 2–4] is abolished on 3’-ara-C containing substrate [lanes 5–7]. Polymerase γ 3’-exonuclease activity [−1 product, lanes 3–4] is also abolished on 3’-ara-C containing substrate [lanes 5–7]. Likewise bypass extension reaction opposite ara-C residue incorporated in the template strand is inhibited [lanes 11–13]. 21-mer substrate (S) [lane #1] and the 20-mer and 22-mer products [P] are indicated. (B) Yields of [+1] extension products generated by pol γ on modified and non-modified substrates are presented as percent mean±SEM of 3 reactions sets. ***P<0.001 indicates different from either extension or bypass reaction assembled with non-modified substrates.