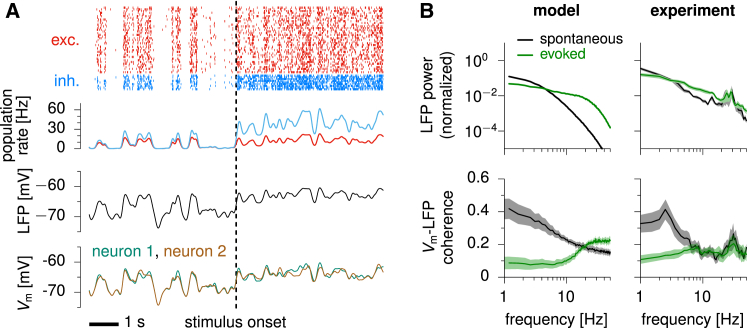
Figure 3.
Modulation of Variability in a Randomly Connected Stochastic Spiking SSN
(A) Top: raster plot of spiking activity, for 40 (out of 4,000) excitatory neurons (red) and 10 (out of 1,000) inhibitory neurons (blue). Upper middle: momentary E and I population firing rates. Lower middle: LFP (momentary population-averaged ). Bottom: of two randomly chosen excitatory neurons. The dashed vertical line marks the onset of stimulus, when h switches from 2 mV to 15 mV. Population firing rates, LFP, and traces were smoothed with a Gaussian kernel of 50 ms width.
(B) Top, normalized LFP power in spontaneous (black) and evoked (green) conditions; bottom, average ( SEM) spectral coherence between single-cell and the LFP; left, model; right, data from V1 of the awake monkey, reproduced from Tan et al. (2014).