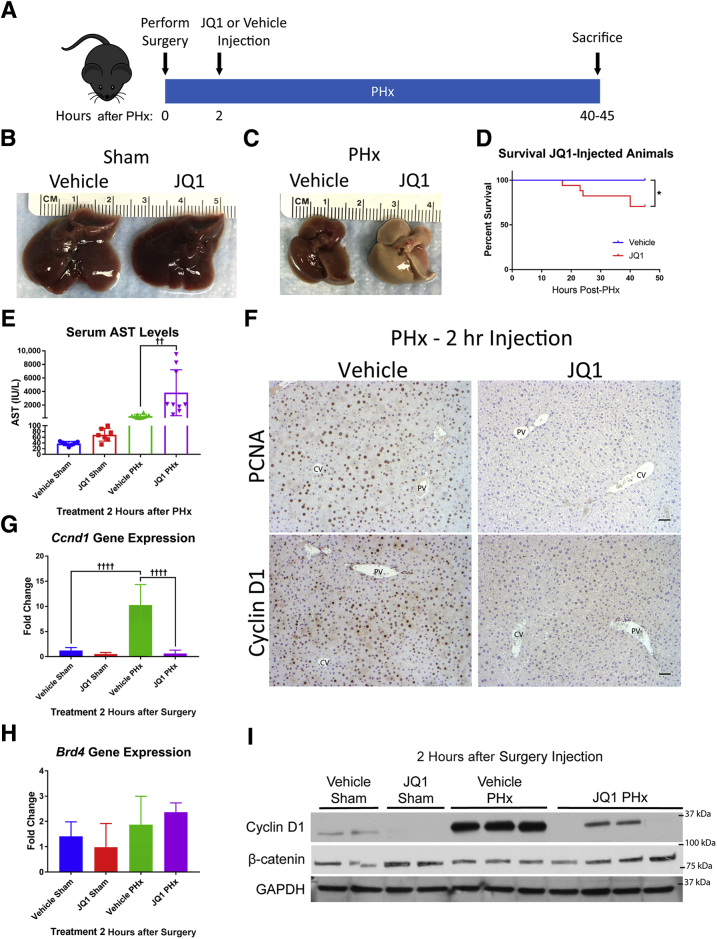
Figure 2.
Injection of JQ1 2 hours after partial hepatectomy (PHx) impaired liver regeneration. A: Schematic for experimental design of injecting JQ1 (50 mg/kg) or vehicle solution 2 hours after PHx and harvesting at 40 to 45 hours after PHx. B: No effect was found on the gross morphology of livers from JQ1-injected sham surgery animals. C: Striking discoloration of the livers of JQ1-injected animals was found 40 hours after PHx. D: Reduced survival of animals injected with JQ1 2 hours after PHx was found. E: No increase in serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST) was found in JQ1-injected sham animals, but a significant increase was found in serum AST in JQ1-injected PHx animals compared with vehicle-injected PHx mice. F: Immunohistochemical staining for proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) and Cyclin D1 revealed robust staining in vehicle-injected controls but virtually no staining in JQ1-injected mice 40 hours after PHx. G: Dramatic up-regulation of Ccnd1 gene expression was found in vehicle-injected animals after PHx, but no up-regulation in JQ1-injected animals. H: No change in Brd4 expression was found after either PHx or JQ1 injection. I: Reduced Cyclin D1 protein was found in JQ1-injected animals compared with vehicle-injected controls, but no reduction in total β-catenin protein levels. Data are expressed as means ± SD. n = 12 vehicle-injected mice (D); n = 17 JQ1-injected mice (D). ∗P < 0.05 (Gehan-Breslow-Wilcoxon test); ††P < 0.01, ††††P < 0.0001 (one-way analysis of variance). Scale bars = 50 μm. CV, central vein; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; PV, portal vein.