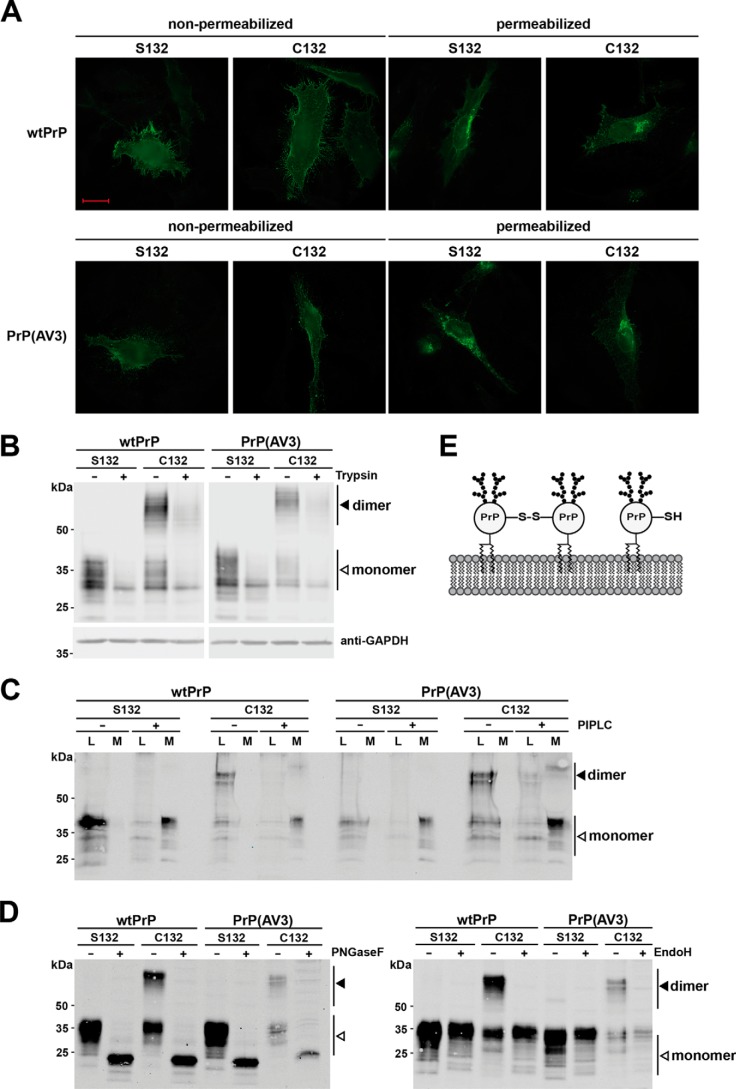
Figure 2.
Covalently linked PrPC dimers are complex glycosylated and GPI-anchored at the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane. A–C, PrP dimers are GPI-anchored at the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane. A, HeLa cells were transiently transfected with the constructs indicated and analyzed by indirect immunofluorescence. Cells were either permeabilized or left nonpermeabilized. PrP constructs were detected with the 3F4 antibody. Scale bar, 20 μm. B, transiently transfected HeLa cells were treated with trypsin for 25 min at room temperature to digest proteins at the plasma membrane. Lysates of treated and untreated cells were analyzed by Western blotting. Detection of cytosolic GAPDH was used to verify that trypsin only digested extracellular proteins. C, transiently transfected N2a cells were incubated for 4 h with and without PIPLC in PBS at 37 °C. PrP present in the cell lysates (L) and the cell culture media (M) were analyzed by Western blotting under nonreducing conditions. PrP was detected by Western blotting using the 3F4 antibody. D, dimerization of PrP does not interfere with complex glycosylation. N2a cells were transiently transfected with the indicated constructs and analyzed by Western blotting. To determine the glycosylation status, lysates were treated either with PNGaseF (+; left panel) that cleaves high-mannose, hybrid, and complex oligosaccharides from N-linked glycoproteins or EndoH, which cleaves only mannose-rich oligosaccharides (+; right panel). Please note that the reaction buffer for PNGaseF and EndoH contains a reducing agent; therefore, only PrP monomers are seen in the PNGaseF- and EndoH-treated samples. White arrowhead, monomer; black arrowhead, dimer. E, schematic representation of monomeric and covalently linked dimeric PrPC located at the plasma membrane. Both fractions are complex glycosylated and inserted into the outer leaflet of plasma membrane via a GPI anchor.