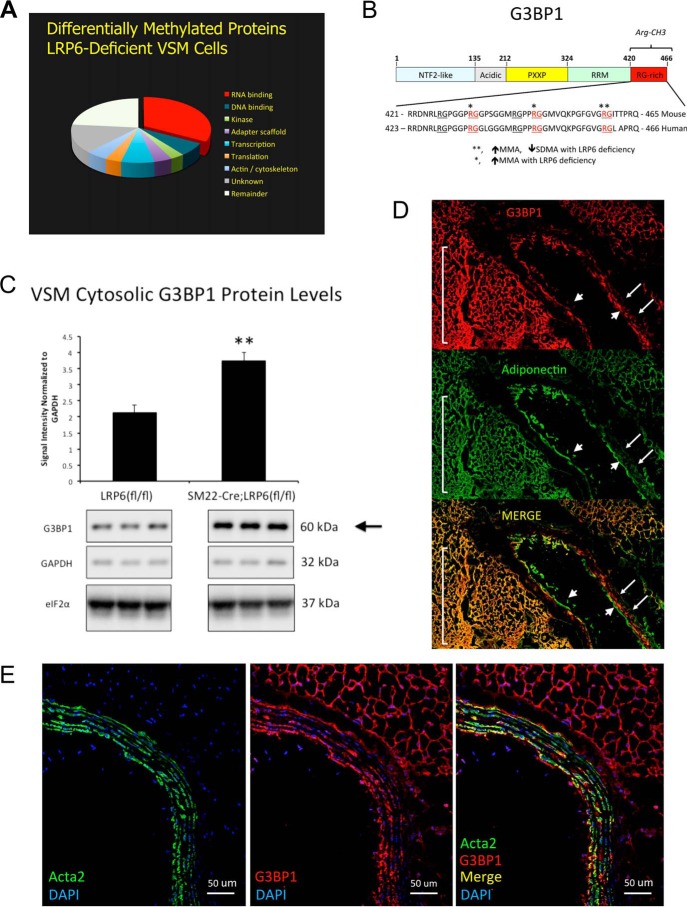
Figure 1.
LRP6 deficiency alters the C-terminal Arg methylation of G3BP1, an RNA-binding protein genetically implicated in human cardiovascular disease. A, arginine methylome analysis reveals a plurality of RNA-binding proteins are regulated by LRP6 deficiency in primary aortic VSM cells. Applying a 2.5-fold threshold for change (2.5-fold increase, 60% decrease) in Arg methylation, 673 VSM proteins were altered with LRP6 deficiency. B, domain structure and C-terminal sequence of murine and corresponding human G3BP1. Residues differentially methylated in VSM with LRP6 deficiency are indicated by asterisks. See also supporting data S1 and S2. C, cytosolic levels of G3BP1 protein are significantly increased in LRP6-deficient VSM cells. D, consistent with results from CARDIoGRAM (18), G3BP1 protein is detected in arterial smooth muscle (arrows) and adjacent fibrofatty adventitia of LDLR-deficient mice fed atherogenic diets (yellow overlays in Merge). Note that although adiponectin is not expressed in endothelial cells, adiponectin protein is taken up by macrovascular endothelial cells (106) and can be immunologically detected (arrowheads). E, confocal co-localization with Acta2 confirms G3BP1 expression in the VSM cells of the tunica media. Note that the fibrofatty adventitial cell G3BP1 expression cell population is Acta2-negative (E) but is adiponectin-positive (D).