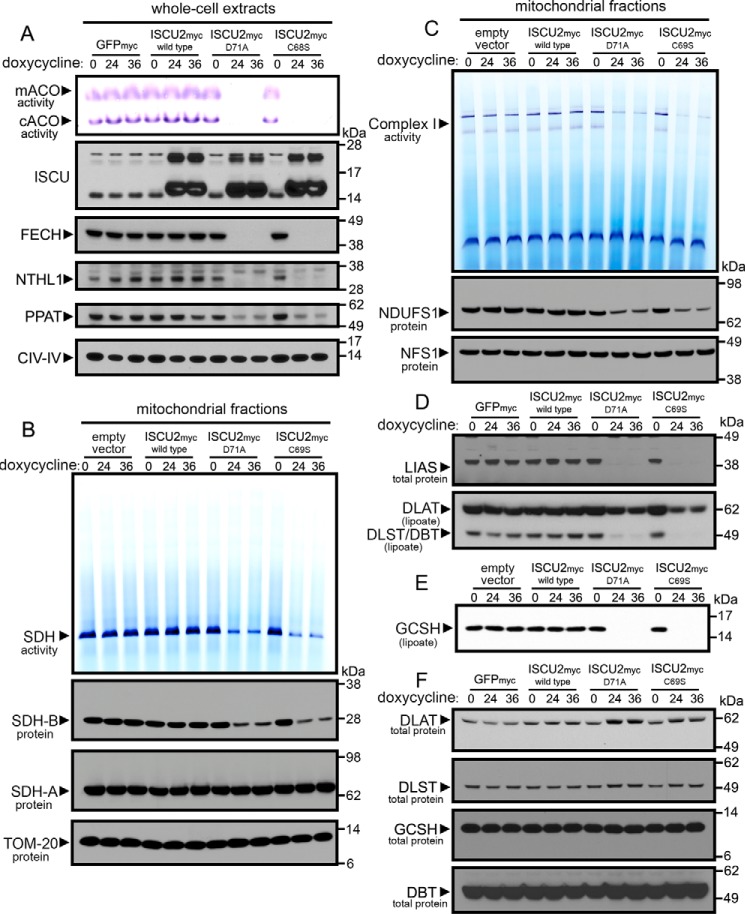
Figure 3.
Widespread loss of Fe-S and lipoate-dependent proteins in cells expressing dominant–negative ISCU mutants. A, cells expressing ISCU2D71A or ISCU2C69S for either 24 or 36 h showed decreased protein levels of Fe-S enzymes in mitochondria (FECH), cytosol (PPAT), and nucleus (NTHL1) and a robust decrease in mitochondrial and cytosolic aconitase activities. B, analysis of complex II activity by in-gel activity assay revealed decreased SDH enzyme activity in cells expressing ISCU2D71A or ISCU2C69S. Immunoblots demonstrated decreased SDHB protein levels, but SDHA protein levels were unchanged in cells expressing ISCU2D71A or ISCU2C69S. Immunoblotting of TOM20 served as the loading control for mitochondrial proteins. C, in-gel assay of NADH-tetrazolium reductase activity showed decreased complex I activity in cells expressing ISCU2D71A or ISCU2C69S for 24 and 36 h. Immunoblotting showed decreased abundance of the complex I core subunit, NDUFS1, but no change in levels of cysteine desulfurase NFS1. Immunoblots revealed decreased protein levels of LIAS and decreased lipoylation of the subunits of pyruvate dehydrogenase (DLST) and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (DLAT) (D) and GCSH (E). F, further immunoblotting showed that total protein levels of these subunits were not decreased.